TAGGED: ansys-hfss, coordinate-systems, coordinates, global coordinate
-
-
April 24, 2024 at 2:06 am
DAQIAN BAO
SubscriberHi Ansys community,
I am generating some data with Ansys AEDT (2023R1) HFSS simulations and trying to do some machine-learning tasks with it.
In the data generation, I set up a relative coordinate for my radar array that the radar array as well as the relative coordinate for the array moves around the global coordinate system. The antennae are defined in the relative coordinate system. The object being detected lies still on the origin of the global coordinate system. I am moving the relative coordinate system in a spherical coordinate with a fixed radius and azimuth and elevation angles are the variables.
At each azimuth and elevation angle, I get the cartesian coordinate of the radar array from the spherical system and point the radar to the object by setting the x-axis of the relative coordinate system to the negative of the position of the origin of the relative coordinate system in the global coordinate system. The "y-point" variable was kept (0,1,0) as default.
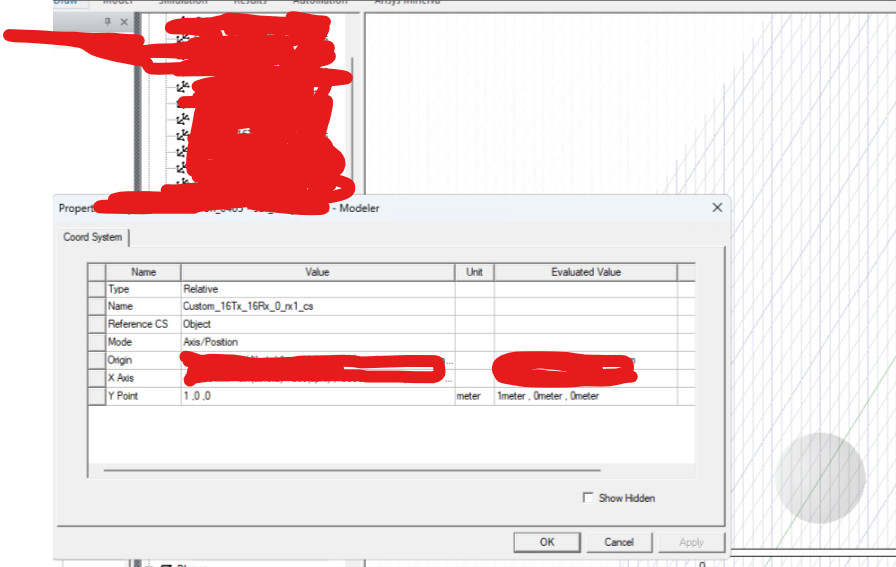
Now I am trying to calculate the position of the antennae in Python but with only the origin of the relative coordinate system and the x-axis of the coordinate system, I only know the plane on which the y and z axes of the relative coordinate system live. In order to find the orientation of the y and z axes of the relative coordinate system, I need to reduce a degree of freedom by correctly interpreting the setting of the y-point in the coordinate system as shown in the screenshot below.
Can someone please let me know what is the correct interpretation of the y-point parameter here in the relative coordinate system?
Best,
DB
-
April 26, 2024 at 11:31 am
dushyant.marathe
Ansys EmployeeHi DAQIAN,
Thanks for posting and asking your query. The placement and orientation of Relative CS is controlled by Axis/Position.
X Axis value controls the direction in which X axis of Relative CS is oriented with respect to Global CS.
For example X-value (1,0,0) orientes X-axis of Relative CS in same direction as X-axis of Global CS, and (0,1,0) means X-axis of Relative CS aligns as Y-axis of Global CS.
Y-point in similar sense orients the Y-axis of Relative CS to that of Global CS. For example Y-value (0,1,0) orientes Y-axis of Relative CS in same direction as Y-axis of Global CS, and (0,0,1) means Y-axis of Relative CS aligns as Z-axis of Global CS.
The X Axis and Y point works in combination and are dependent on each other. For example keeping X Axis and Y point values same (1,0,0) & (1,0,0) tool will throgh the error saying "RelativeCSParameters: X and Y vectors are parallel."
Thanks,
-
- The topic ‘Y Point in relative coordinate system’ is closed to new replies.



-
3472
-
1057
-
1051
-
934
-
897

© 2025 Copyright ANSYS, Inc. All rights reserved.