-
-
May 13, 2020 at 8:10 am
akiii
SubscriberHi everyone,
I am trying to simulate tutorial 5 of transient compressible flow through a two-dimensional nozzle.
I change the conditions of tutorial 5 to make it easy and to understand the difference between density based and pressure based.
?to make it easy : boundary condition using UDF→Inlet pressure 1.5 Pa and outlet pressure is 1.0 Pa
?to understand the difference between density based and pressure based :
density based → pressure based
It does not work when I use the conditions, instead it give me error like an image: "Floating point exception" immediately when I start simulation.
Can anyone help me as to how to fix the problem ?
Tutorial URL ↓
A error image ↓
-
May 13, 2020 at 8:11 am
akiii
SubscriberError coad ↓
Adapting mesh (Gradient Adaption of pressure)...
Based on specified limits, either too many
or too few cells were marked for refinement.
Thresholds were re-adjusted to:
Coarsening: 0.44541
Refinement: 0.79253
Based on specified limits, either too many
or too few cells were marked for refinement.
Thresholds were re-adjusted to:
Coarsening: 0.63048
Refinement: 0.83219
done.
iter continuity x-velocity y-velocity energy k omega time/iter
500 1.9240e-02 3.8643e-05 2.3561e-05 3.4017e-06 8.8101e-04 7.2091e-04 0:00:00 10
Stabilizing pressure correction to enhance linear solver robustness.
Divergence detected in AMG solver: pressure correction Stabilizing pressure correction to enhance linear solver robustness.
Divergence detected in AMG solver: pressure correction Stabilizing k to enhance linear solver robustness.
Divergence detected in AMG solver: k Stabilizing omega to enhance linear solver robustness.
Divergence detected in AMG solver: omega Stabilizing temperature to enhance linear solver robustness.
Divergence detected in AMG solver: temperature
Divergence detected in AMG solver: pressure correction
Divergence detected in AMG solver: pressure correction
Divergence detected in AMG solver: k
Divergence detected in AMG solver: omega
Divergence detected in AMG solver: temperature
Divergence detected in AMG solver: pressure correction
Divergence detected in AMG solver: pressure correction
Divergence detected in AMG solver: k
Divergence detected in AMG solver: omega
Divergence detected in AMG solver: temperature
Divergence detected in AMG solver: pressure correction
Divergence detected in AMG solver: pressure correction
Divergence detected in AMG solver: k
Divergence detected in AMG solver: omega
Divergence detected in AMG solver: temperature
Error at host: floating point exception
Error at Node 0: floating point exception
Error at Node 1: floating point exception
Error at Node 2: floating point exception
Error at Node 3: floating point exception
Error: floating point exception
Error Object: #f
-
May 13, 2020 at 1:19 pm
Karthik Remella
AdministratorHello,
This is a compressible flow problem you are solving. Right after you obtain a steady state solution, the max velocity in your domain is nearly equal to the speed of sound in air (Mach 1). Even though the pressure-based solvers in Fluent is robust, I'd stick to using the density-based solver for this example. You are running into convergence issues with the problem because of the change in solver settings.
The primary difference between the two is the following:
The pressure field is obtained from the equation of state in the density-based solver and the continuity equation is used to get the density. However, in the pressure-based solver, the pressure correction equation is used to solve for the pressure field. If you are looking for additional information about this, please refer to the following section on the Fluent Theory Guide.
Thanks.
Best,
Karthik
-
May 14, 2020 at 8:49 am
akiii
SubscriberThanks for your reply. It may be long and poor English, but I'm very happy to help.
About this tutorial 5, because the max velocity in a compressible flow is nearly equal to the speed of sound in air (Mach 1), it will diverge when I use pressure based solver , right? Then, which solver is appropriate, density based or pressure based, when the Mach number in a compressible subsonic flow is 0.3~1 ?
(0.3 is boundary whether it is a compressible flow, and 1 is boundary whether it is a supersonic flow)
I have seen various explanations of pressure based and density based in Ansys HP, but I do not understand why difference in the equation cause difference in the ease of convergence depending on the max velocity in the flow ,namely, the Mach number.
--
I have been studying High-Speed Impinging Air Jet and simulating this shape A under condition (I)
Nozzle shape A (mm) depth 1.256mm
Three-dimensional incompressible viscous flow
Condition (I)
?Transient
?Pressure based
?Energy on
?DES SST-k-ω
?Air Density is constant
?Inlet Gauge Total Pressure : 11kpa
?Outlet Gauge Total Pressure : 0kpa (Atmospheric pressure)
?Scheme : PISO
?Time step size : 3e-08
?Number of meshes : 2 million
?Time step : 100,000 steps
?Calculation time : About 2 months
I finally want to calculate the new shape B below
Nozzle shape B (mm) depth 1.256mm
Three-dimensional compressible viscous flow
shape B -1 : Inlet Gauge Total Pressure is changed to 25kpa or 50kpa
Or
shape B -2 : A slit with a width of 0.4mm is changed to 0.2mm
However, I don't know how to change the condition (I), and which solver is appropriate density based or pressure based. So I did tutorial 5 but I can't understand
I tried simulating shape A under different condition (II) in the past
Condition (II)
?Pressure based → Density based
?Air Density is constant → Ideal gas
?Time step size 3e-08 → 1.5e-08
?Others are same as the condition (I)
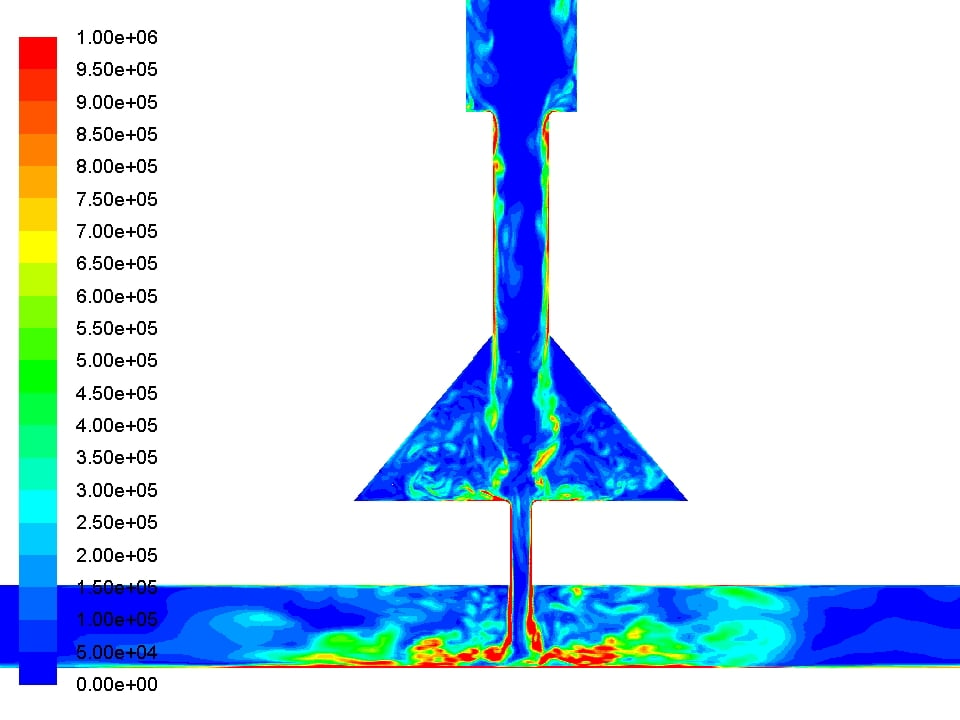
Even though they have the same nozzle shape A, there is a difference in the vorticity image between the condition (I) and (II).
Condition (I) ↓
Condition(II) ↓
In (I), we can see small wavelength vorticity.
In (II), we can see beautiful round big vorticity but can’t see the small wavelength vorticity like (I).
I do not know what caused this difference in vorticity. Is it solver?
Help me.
-
- The topic ‘Stabilizing pressure correction to enhance linear solver robustness.’ is closed to new replies.



-
4888
-
1587
-
1386
-
1242
-
1021

© 2026 Copyright ANSYS, Inc. All rights reserved.