-
-
January 10, 2025 at 1:26 pm
m202373352
Subscriber老师您好,我在官网下载了“Inverse design of y-branch”的案例,并尝试将其修改成我自己的几何结构并进行优化,目前遇到了如下问题,烦请老师进行解答:
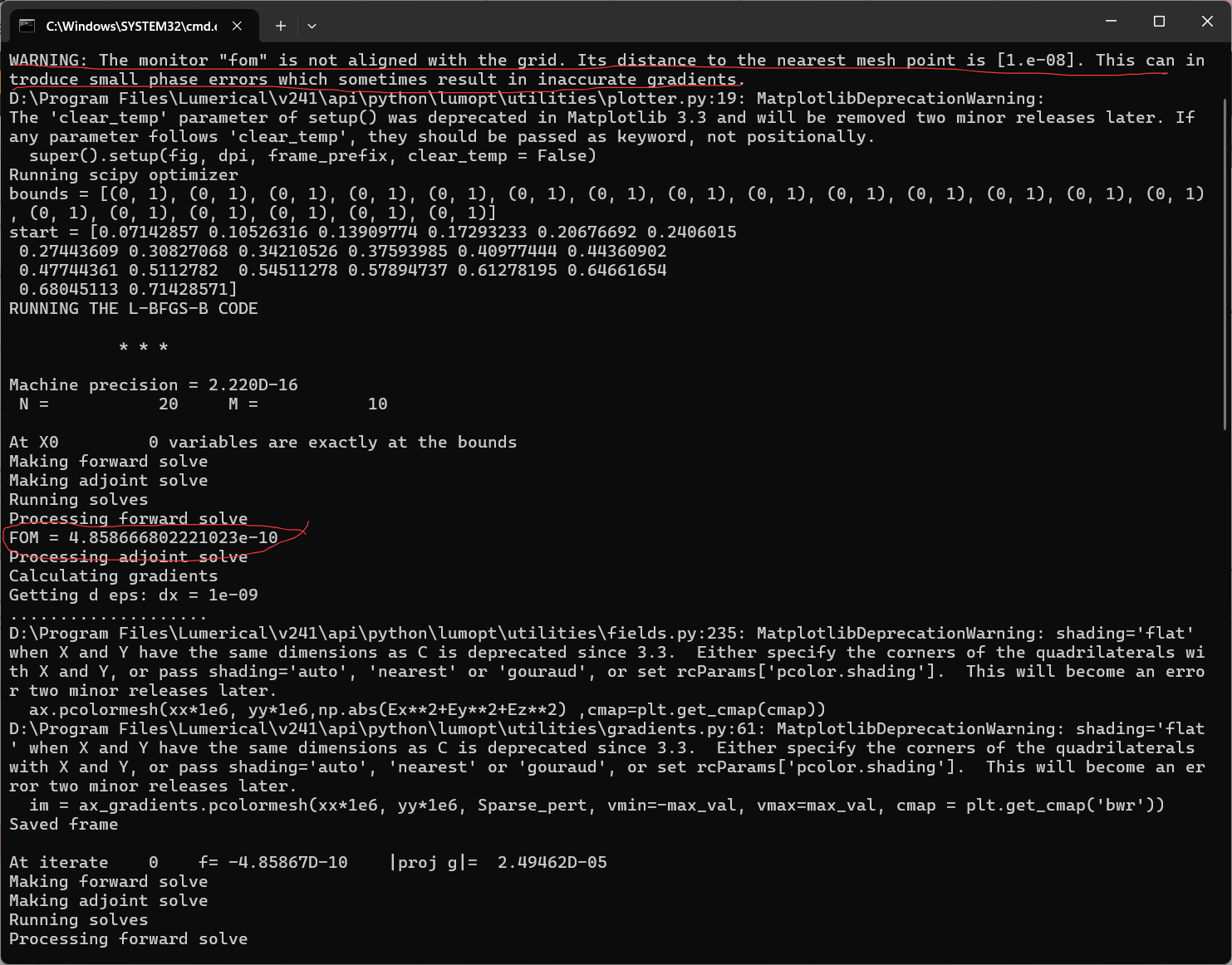
1.再将几何参数等修改为我自己的结构时,运行代码会出现如下报错:WARNING: The monitor "fom" is not aligned with the grid. Its distance to the nearest mesh point is [1.e-08]. This can introduce small phase errors which sometimes result in inaccurate gradients.但是运行案例时就没有这个问题。我也尝试在fom监视器处加一个mesh,以强制让其与网格对齐,但是这又会出现新的报错:D:\Program Files\Lumerical\v241\api\python\lumapi.py:160: UserWarning: Multiple objects named '::model::mesh'. Use of this object may give unexpected results.warnings.warn(message)。因此想请教老师,在形状优化当中,fom监视器处究竟需不需要或者说能不能加mesh以强制对齐网格?如果不能,那上述问题该如何解决?
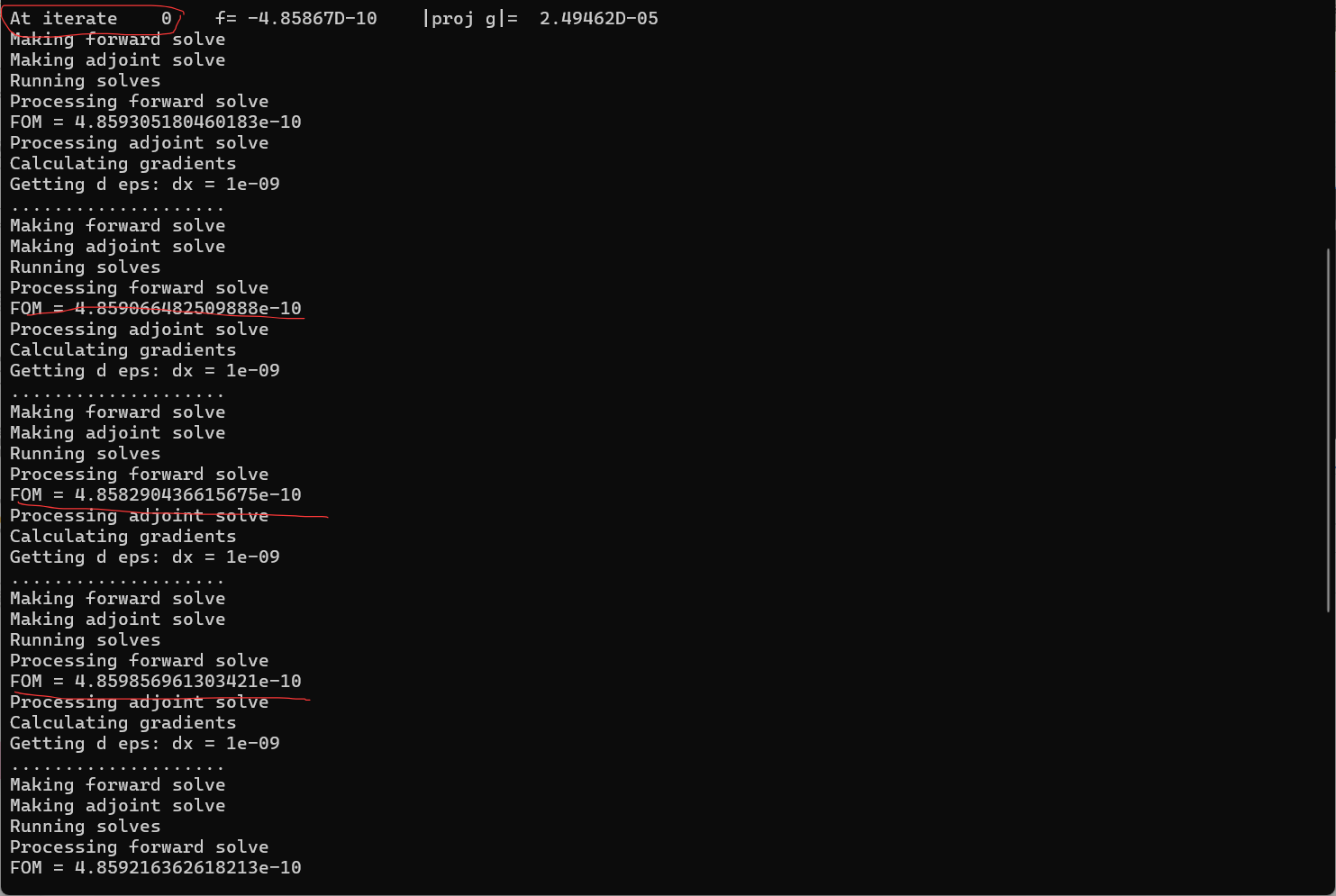
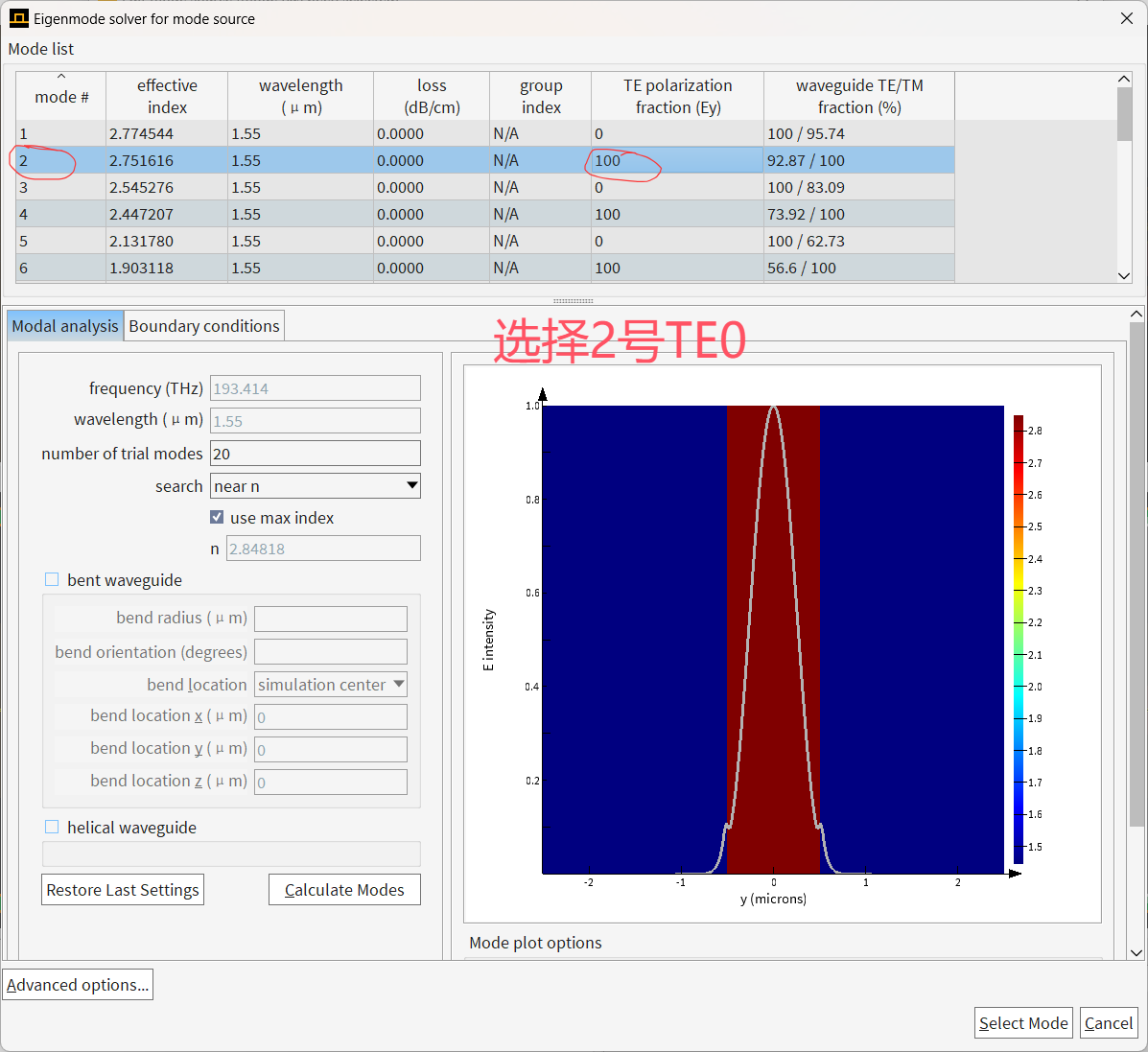
2.我在运行仿真时,并没有采用对称边界条件,因为我所选的模式光源关于y轴并不对称。举例说,我想选择TE0模作为输入,输出fom同样也选择TE0模作为监视对象,这种情况当我选择模式的序号,输入光源模式序号为2,输出fom模式序号选择3,但是发现,当直接选择模式序号时,优化会出现问题,发现迭代一直卡在第0代,并且fom值非常小(1e-10的数量级),并且几代就结束了优化,但是感觉并没有真正的优化。请问这个问题是什么原因造成的呢,应该如何解决?因为所涉及到的输入有高阶模式,因为不能直接选择“fundamental mode”。当选择输入光源和输出监视器fom均选择“fundamental mode“时,优化可以进行,但还是会出现WARNING: The monitor "fom" is not aligned with the grid. Its distance to the nearest mesh point is [1.e-08]. This can introduce small phase errors which sometimes result in inaccurate gradients.的警告。
下面给出了我仿真的代码以及相应的报错等相关截图。以上问题已经困惑了我好久,真诚希望老师能在百忙之中检阅并予以知道,非常感谢!!!!
import lumapi
import numpy as np
from scipy.constants import c
def y_branch_init_(mode):
## CLEAR SESSION
mode.switchtolayout()
mode.selectall()
mode.delete()
## SIM PARAMS
size_x=6e-6;
size_y=5e-6;
mesh_x=20e-9;
mesh_y=20e-9;
finer_mesh_size_x=5.5e-6;
finer_mesh_size_y=4.5e-6;
mesh_accuracy=4;
lam_c = 1.550e-6;
## MATERIAL
opt_material=mode.addmaterial('Dielectric');
mode.setmaterial(opt_material,'name','Si: non-dispersive');
n_opt = mode.getindex('Si (Silicon) - Palik',c/lam_c);
mode.setmaterial('Si: non-dispersive','Refractive Index',n_opt);
sub_material=mode.addmaterial('Dielectric');
mode.setmaterial(sub_material,'name','SiO2: non-dispersive');
n_sub = mode.getindex('SiO2 (Glass) - Palik',c/lam_c);
mode.setmaterial('SiO2: non-dispersive','Refractive Index',n_sub);
mode.setmaterial('SiO2: non-dispersive',"color", np.array([0, 0, 0, 0]));
## GEOMETRY
#INPUT WAVEGUIDE
mode.addrect();
mode.set('name','input wg');
mode.set('x span',3e-6);
mode.set('y span',1e-6);
mode.set('z span',220e-9);
mode.set('y',0);
mode.set('x',-4e-6);
mode.set('z',0);
mode.set('material','Si: non-dispersive');
#OUTPUT WAVEGUIDES
mode.addrect();
mode.set('name','output wg top');
mode.set('x span',3e-6);
mode.set('y span',1e-6);
mode.set('z span',220e-9);
mode.set('y',0.9e-6);
mode.set('x',4e-6);
mode.set('z',0);
mode.set('material','Si: non-dispersive');
mode.addrect();
mode.set('name','output wg bottom');
mode.set('x span',3e-6);
mode.set('y span',1e-6);
mode.set('z span',220e-9);
mode.set('y',-0.9e-6);
mode.set('x',4e-6);
mode.set('z',0);
mode.set('material','Si: non-dispersive');
mode.addrect();
mode.set('name','sub');
mode.set('x span',11e-6);
mode.set('y span',11e-6);
mode.set('z span',10e-6);
mode.set('y',0);
mode.set('x',0);
mode.set('z',0);
mode.set('material','SiO2: non-dispersive');
mode.set('override mesh order from material database',1);
mode.set('mesh order',3);
mode.set('alpha',0.8);
## varFDTD
mode.addvarfdtd();
mode.set('mesh accuracy',mesh_accuracy);
mode.set('x min',-size_x/2);
mode.set('x max',size_x/2);
mode.set('y min',-size_y/2);
mode.set('y max',size_y/2);
#mode.set('force symmetric y mesh',1);
#mode.set('y min bc','Anti-Symmetric');
mode.set('z',0);
mode.set('effective index method','variational');
mode.set('can optimize mesh algorithm for extruded structures',1);
mode.set('clamp values to physical material properties',1);
mode.set('x0',-2.8e-6);
mode.set('number of test points',4);
mode.set('test points',np.array([[0, 0],[2.8e-6, 1e-6], [2.8e-6, -1e-6], [2.8e-6, 0]]));
## SOURCE
mode.addmodesource();
mode.set('direction','Forward');
mode.set('injection axis','x-axis');
#mode.set('polarization angle',0);
mode.set('y',0);
mode.set("y span",size_y);
mode.set('x',-2.75e-6);
mode.set('center wavelength',1550e-9);
mode.set('wavelength span',0);
mode.set('mode selection','user select');
mode.set('selected mode number', 2);
## MESH IN OPTIMIZABLE REGION
mode.addmesh();
mode.set('x',0);
mode.set('x span',finer_mesh_size_x);
mode.set('y',0);
mode.set('y span',finer_mesh_size_y);
mode.set('dx',mesh_x);
mode.set('dy',mesh_y);
## OPTIMIZATION FIELDS MONITOR IN OPTIMIZABLE REGION
mode.addpower();
mode.set('name','opt_fields');
mode.set('monitor type','2D Z-normal');
mode.set('x',0);
mode.set('x span',finer_mesh_size_x - 0.1e-6);
mode.set('y',0);
mode.set('y span',finer_mesh_size_y - 0.1e-6);
mode.set('z',0);
## FOM FIELDS
mode.addpower();
mode.set('name','fom');
mode.set('monitor type','Linear Y');
mode.set('x',2.75e-6);
mode.set('y',0);
mode.set('y span',size_y);
mode.set('z',0);
#mode.addmesh();
#mode.set("name","fom_mesh");
#mode.set("x",2.75e-6);
#mode.set("x span",2*mesh_x);
#mode.set("y",0);
#mode.set("y span",size_y);
#mode.set("z",0);
##set("z span",240e-9);
#mode.set("override x mesh",1); ##
#mode.set("override y mesh",0); ##
#mode.set("override z mesh",0); ##
#mode.set("dx",mesh_x);
#mode.addmodeexpansion();##
#mode.set("name","mode_expansion");
#mode.set("monitor type",2); # 1 = linear X, 2 = linear Y
#mode.set("x", 2.75e-6);
#mode.set("z",0);
#mode.set("y", 0);
#mode.set("y span",size_y);
#mode.select("mode_expansion");
#mode.setexpansion("input", "fom");
#mode.set("mode selection","user select"); # use the 'user select' option
#mode.seteigensolver("use max index",1); # specify a custom value for 'n'
#mode.updatemodes(3);
if __name__ == "__main__":
mode = lumapi.MODE(hide = False)
y_branch_init_(mode)
input('Press Enter to escape...')
优化代码:
import os, sys
import numpy as np
import scipy as sp
import lumapi
from lumopt.utilities.wavelengths import Wavelengths
from lumopt.geometries.polygon import FunctionDefinedPolygon
from lumopt.utilities.materials import Material
from lumopt.figures_of_merit.modematch import ModeMatch
from lumopt.optimizers.generic_optimizers import ScipyOptimizers
from lumopt.optimization import Optimization
######## BASE SIMULATION ########
sys.path.append(os.path.dirname(__file__))
from varFDTD_y_branch import y_branch_init_
y_branch_base = y_branch_init_
######## DIRECTORY FOR GDS EXPORT #########
example_directory = os.getcwd()
######## SPECTRAL RANGE #########
wavelengths = Wavelengths(start = 1530e-9, stop = 1565e-9, points = 8)
######## DEFINE OPTIMIZABLE GEOMETRY ########
# The class FunctionDefinedPolygon needs a parameterized Polygon (with points ordered
# in a counter-clockwise direction). Here the geometry is defined by 10 parameters defining
# the knots of a spline, and the resulting Polygon has 200 edges, making it quite smooth.
# Define the span and number of points
initial_points_x = np.linspace(-2.5e-6, 2.5e-6, 20)
initial_points_y = np.linspace(0.5e-6, 1.4e-6, initial_points_x.size)
def splitter(params):
''' Defines a taper where the paramaters are the y coordinates of the nodes of a cubic spline. '''
## Include two set points based on the initial guess. The should attach the optimizeable geometry to the input and output
points_x = np.concatenate(([initial_points_x.min() - 0.01e-6], initial_points_x, [initial_points_x.max() + 0.01e-6]))
points_y = np.concatenate(([initial_points_y.min()], params, [initial_points_y.max()]))
## Up sample the polygon points for a smoother curve. Some care should be taken with interp1d object. Higher degree fit
# "cubic", and "quadratic" can vary outside of the footprint of the optimization. The parameters are bounded, but the
# interpolation points are not. This can be particularly problematic around the set points.
n_interpolation_points = 200
polygon_points_x = np.linspace(min(points_x), max(points_x), n_interpolation_points)
interpolator = sp.interpolate.interp1d(points_x, points_y, kind = 'cubic')
polygon_points_y = interpolator(polygon_points_x)
### Zip coordinates into a list of tuples, reflect and reorder. Need to be passed ordered in a CCW sense
polygon_points_up = [(x, y) for x, y in zip(polygon_points_x, polygon_points_y)]
polygon_points_down = [(x, -y) for x, y in zip(polygon_points_x, polygon_points_y)]
polygon_points = np.array(polygon_points_up[::-1] + polygon_points_down)
return polygon_points
# L-BFGS methods allows the parameters to be bound. These should enforse the optimization footprint defined in the setup
bounds = [(0.4e-6, 1.8e-6)] * initial_points_y.size
#Load from 2D results if availble
try:
prev_results = np.loadtxt('2D_parameters.txt')
except:
print("Couldn't find the file containing 2D optimization parameters. Starting with default parameters")
prev_results = initial_points_y
# Set device and cladding materials, as well as as device layer thickness
eps_in = Material(name = 'Si: non-dispersive', mesh_order = 2)
eps_out = Material(name = 'SiO2: non-dispersive', mesh_order = 3)
depth = 220.0e-9
# Initialize FunctionDefinedPolygon class
polygon = FunctionDefinedPolygon(func = splitter,
initial_params = prev_results,
bounds = bounds,
z = 0.0,
depth = depth,
eps_out = eps_out, eps_in = eps_in,
edge_precision = 5,
dx = 1.0e-9)
######## FIGURE OF MERIT ########
fom = ModeMatch(monitor_name = 'fom',
mode_number = 3,
direction = 'Forward',
target_T_fwd = lambda wl: np.ones(wl.size),
norm_p = 1)
######## OPTIMIZATION ALGORITHM ########
optimizer = ScipyOptimizers(max_iter = 30,
method = 'L-BFGS-B',
#scaling_factor = scaling_factor,
pgtol = 1.0e-5,
ftol = 1.0e-5,
#target_fom = 0.0,
scale_initial_gradient_to = 0.0)
######## PUT EVERYTHING TOGETHER ########
opt = Optimization(base_script = y_branch_base,
wavelengths = wavelengths,
fom = fom,
geometry = polygon,
optimizer = optimizer,
use_var_fdtd = True,
hide_fdtd_cad = False,
use_deps = True,
plot_history = True,
store_all_simulations = False)
######## RUN THE OPTIMIZATION ########
results = opt.run()
######## SAVE THE BEST PARAMETERS TO FILE ########
np.savetxt('../2D_parameters.txt', results[1])
######## EXPORT OPTIMIZED STRUCTURE TO GDS ########
gds_export_script = str("gds_filename = 'y_branch_2D.gds';" +
"top_cell = 'model';" +
"layer_def = [1, {0}, {1}];".format(-depth/2, depth/2) +
"n_circle = 64;" +
"n_ring = 64;" +
"n_custom = 64;" +
"n_wg = 64;" +
"round_to_nm = 1;" +
"grid = 1e-9;" +
"max_objects = 10000;" +
"Lumerical_GDS_auto_export;")
with lumapi.MODE(hide = False) as mode:
mode.cd(example_directory)
y_branch_init_(mode)
mode.addpoly(vertices = splitter(results[1]))
mode.set('x', 0.0)
mode.set('y', 0.0)
mode.set('z', 0.0)
mode.set('z span', depth)
mode.set('material','Si: non-dispersive')
mode.save("y_branch_2D_FINAL")
input('Enter...')
mode.eval(gds_export_script)
-
January 15, 2025 at 11:46 am
m202373352
Subscriber以上问题已经困惑了我好久,真诚希望老师能在百忙之中检阅并予以知道,非常感谢!!!!
-
January 16, 2025 at 3:06 am
GuanYo Dong
Subscriber你好
第一個指出的問題,得讓局部加的mesh name那一欄位不重複,多個編號之類的,不要讓每個都叫做mesh,這在後續select的時候容易出錯選到多個。
我們試試看比較定義座標的時候, 腳本中避免算了多次A/2,那我們讓軟件先把A/2給成一個代號每次給到軟件的位置,因為多次算可能會造成浮點數最後一個位數計算偏差,就是您看到1e-8。第二個除了網格對不齊的問題外,我們選模式在Y-brench 出口端的兩個端口,應該各自放一個monitor去偵測,並且各自選擇模式。這三個位置的monitor也應該要一樣大,且跟結構中心對齊,此時應該選到一樣的模式編號,無論是不是自選的。
莎益博 董冠佑
-
January 16, 2025 at 8:04 am
m202373352
Subscriber您的回复已经收到,非常感谢!请问"我們選模式在Y-brench 出口端的兩個端口,應該各自放一個monitor去偵測,並且各自選擇模式。這三個位置的monitor也應該要一樣大,且跟結構中心對齊"您这句话想表达的是什么意思,不是很理解?您所指的“三个位置”是哪三个位置?在Y-branch两个输出端分别放置一个监视器,还有哪个地方需要放吗?
还有就是为什么不可以像案例中那样,在输出端放置一个阔度比较大的、覆盖两个输出端口的监视器呢?再次感谢您的回复,祝工作顺利,身体健康!
-
January 16, 2025 at 12:07 pm
GuanYo Dong
Subscriber你好
不好意思這個案例mode expantion的用法跟一般比較不同,他確實是兩個出口端共用一個mode expantion,並且是此結構的基模,兩個一起看總透過率。
要分析s參數的時候才一定要一個端口一個mode expantion.
另外我發現代碼varFDTD_y_branch.py,並沒有在建立基本文件的步驟加入mode expantion,但在優化文件中有 ,那你在這段落加入了,可以在優化中途確認一下是否有多一個?
如果有多,也要確認軟件抓取哪一個數據?
案例代碼y_branch_opt_2D.py就可以直接改要分析的模式,我選不是基模,可以有結果但不同的模式最佳的情況不同,這個模式就沒有官網的基模好。
所以不同模式也可能結果不好。 -
January 17, 2025 at 4:13 am
m202373352
Subscriber非常感谢您的回复,但是问题还是没有解决,还要跟您再请教一下。
首先,我想做一个能同时实现TE0模和TE1模分束的Y-branch结构,因而我在选择光源mode number和fom的“mode_number”时会涉及TE1模的选择,不能只选择“fundamental mode”。因为我也不知道在模式扩展监视器中应具体选择哪个模式序号,因而在fom监视器的位置放置了一个和fom监视器尺寸相同并且将fom监视器作为"Monitors for expansion"输入,用来预先确定要选择的模式序号,但是在后续开始优化的时候,我是将刚才提到的模式扩展监视器注释掉的,因而在生成的仿真文件中只有文件自动生成的“fom_mode_exp”监视器。
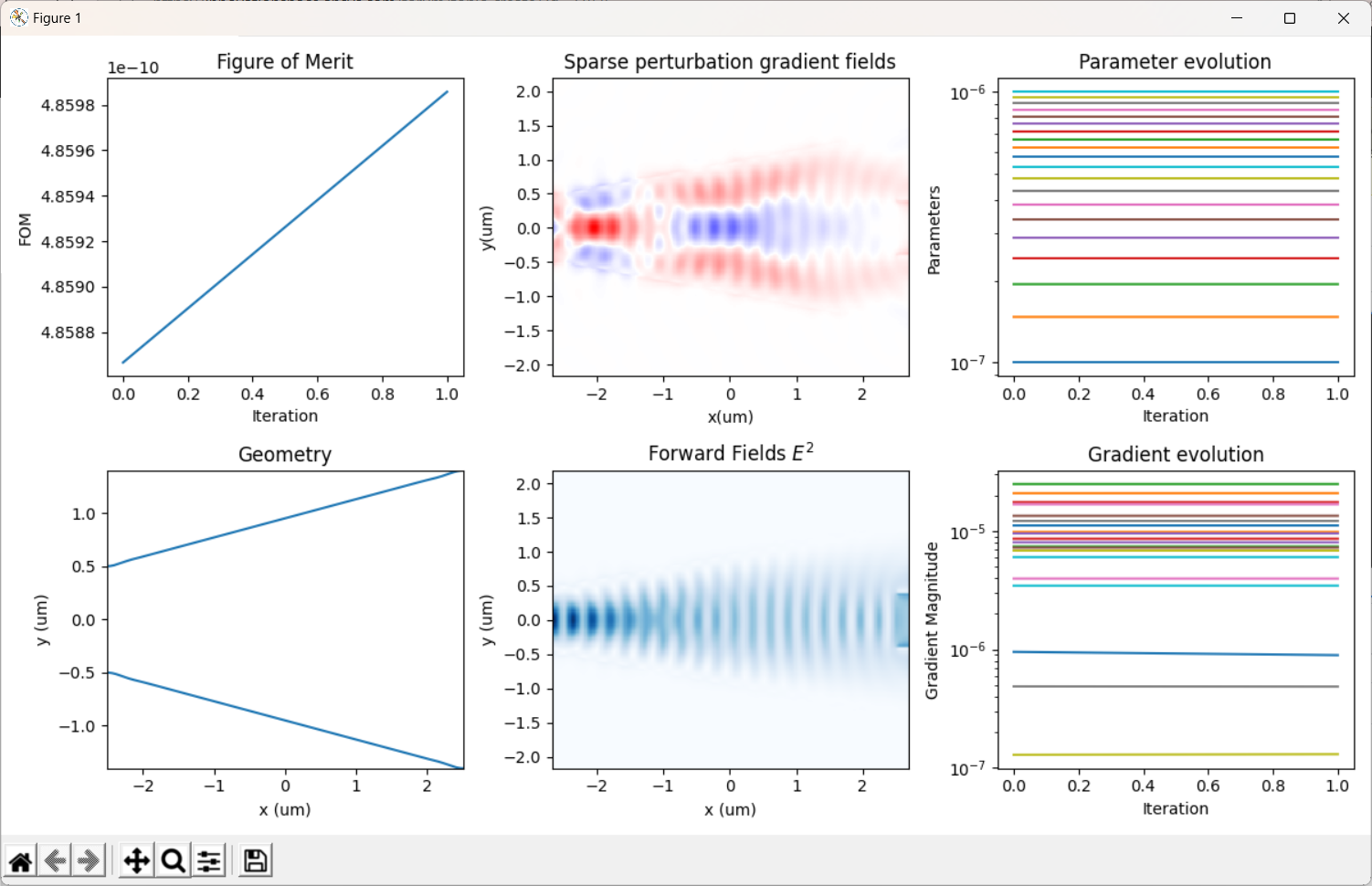
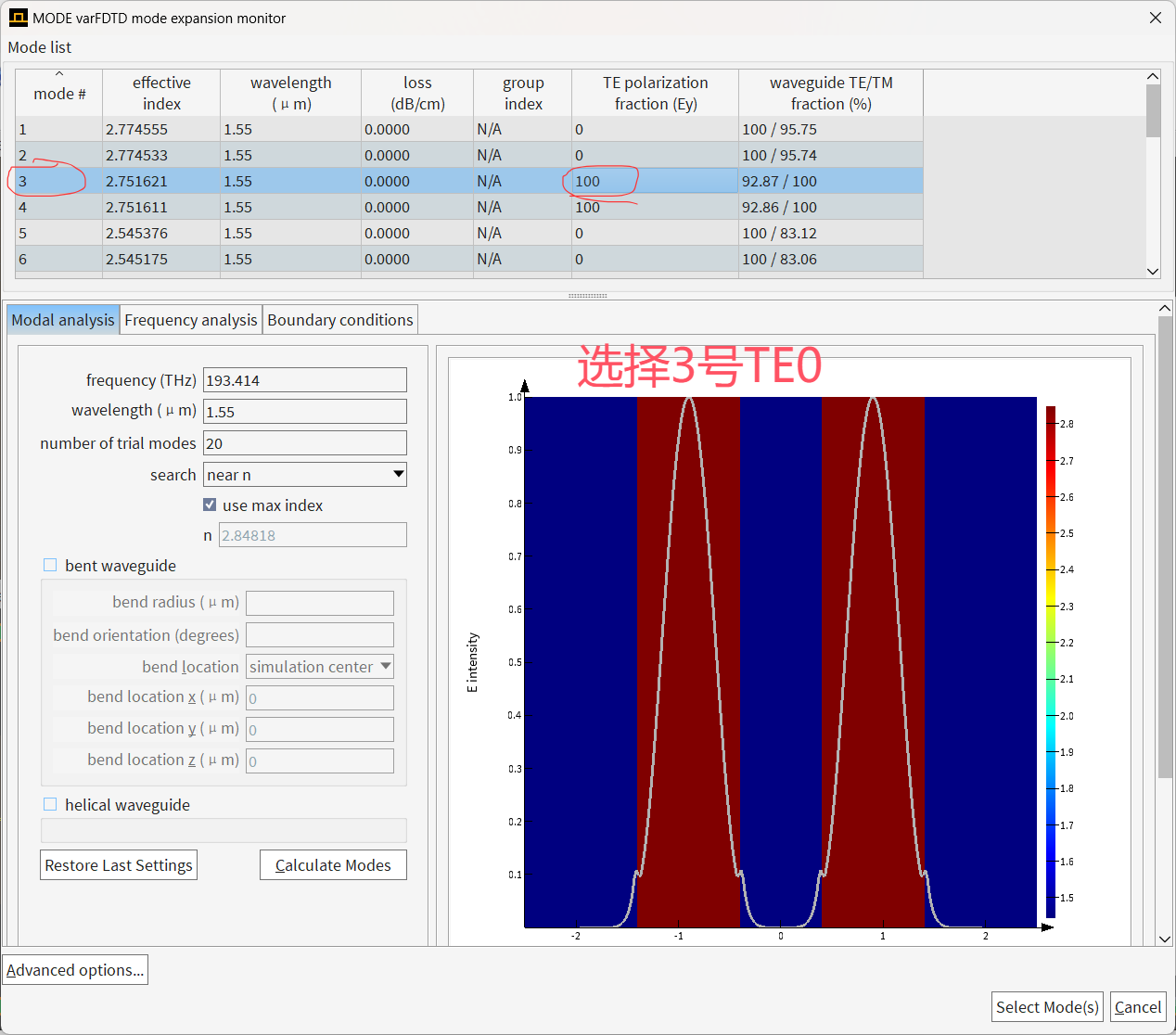
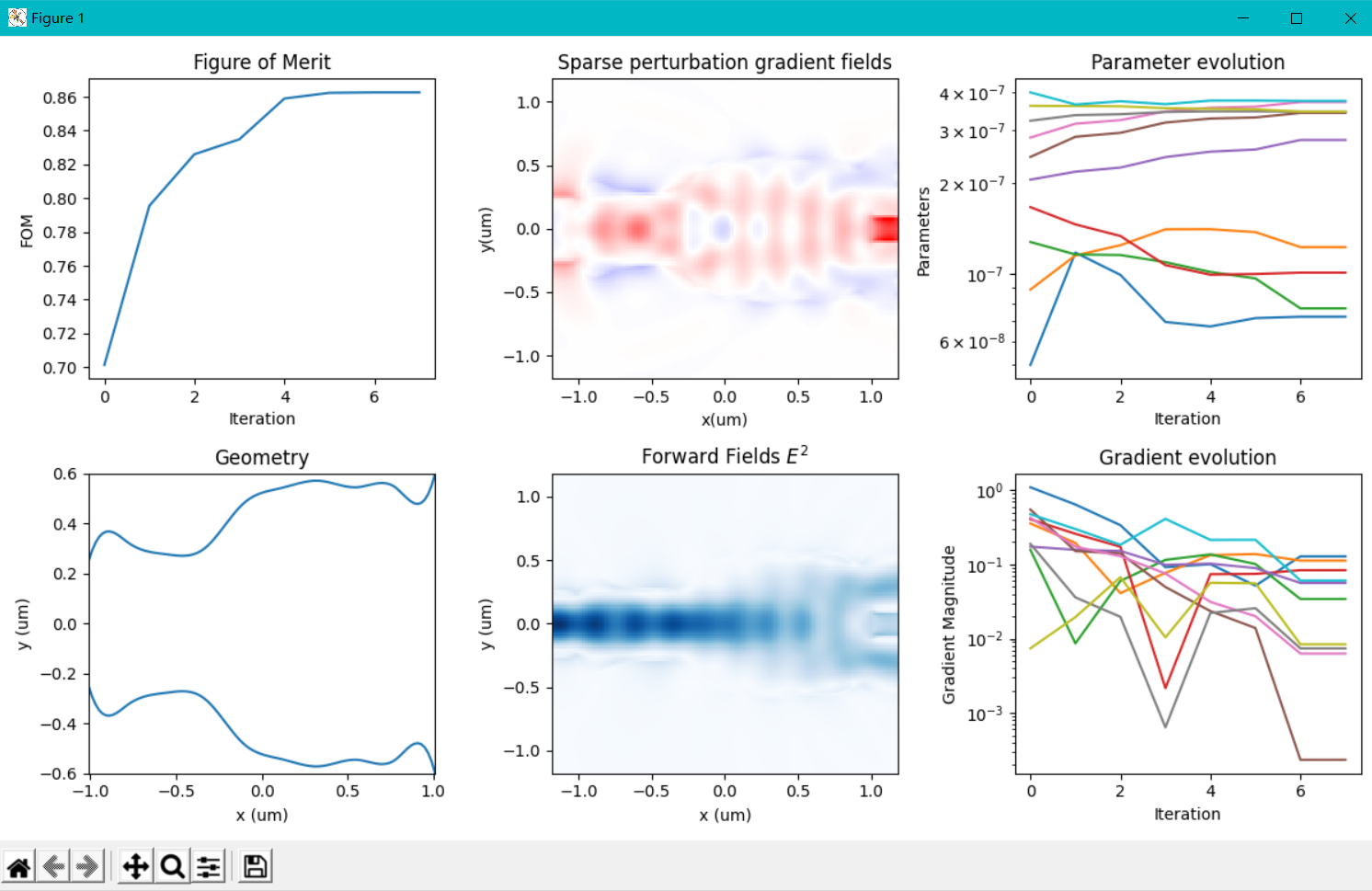
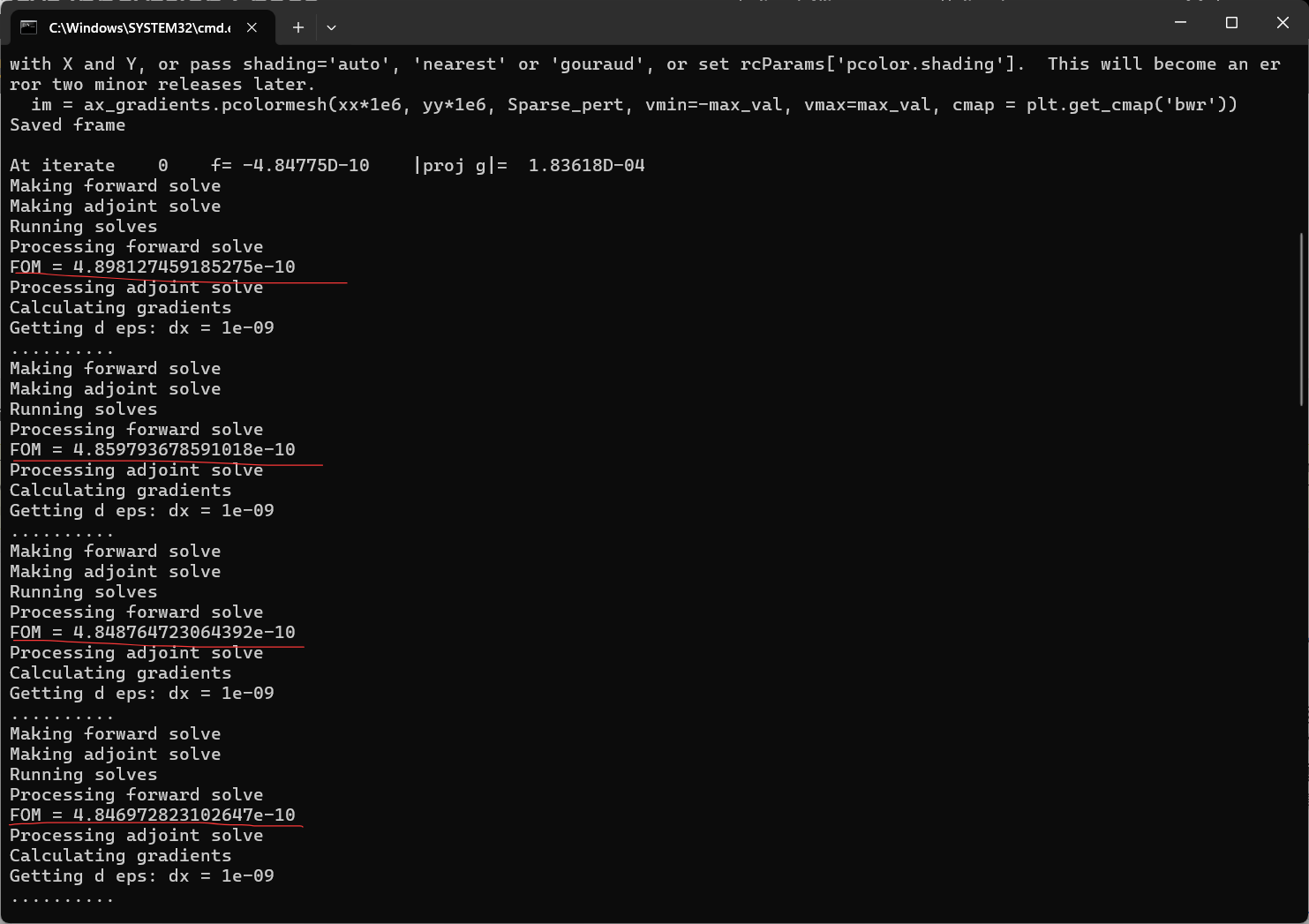
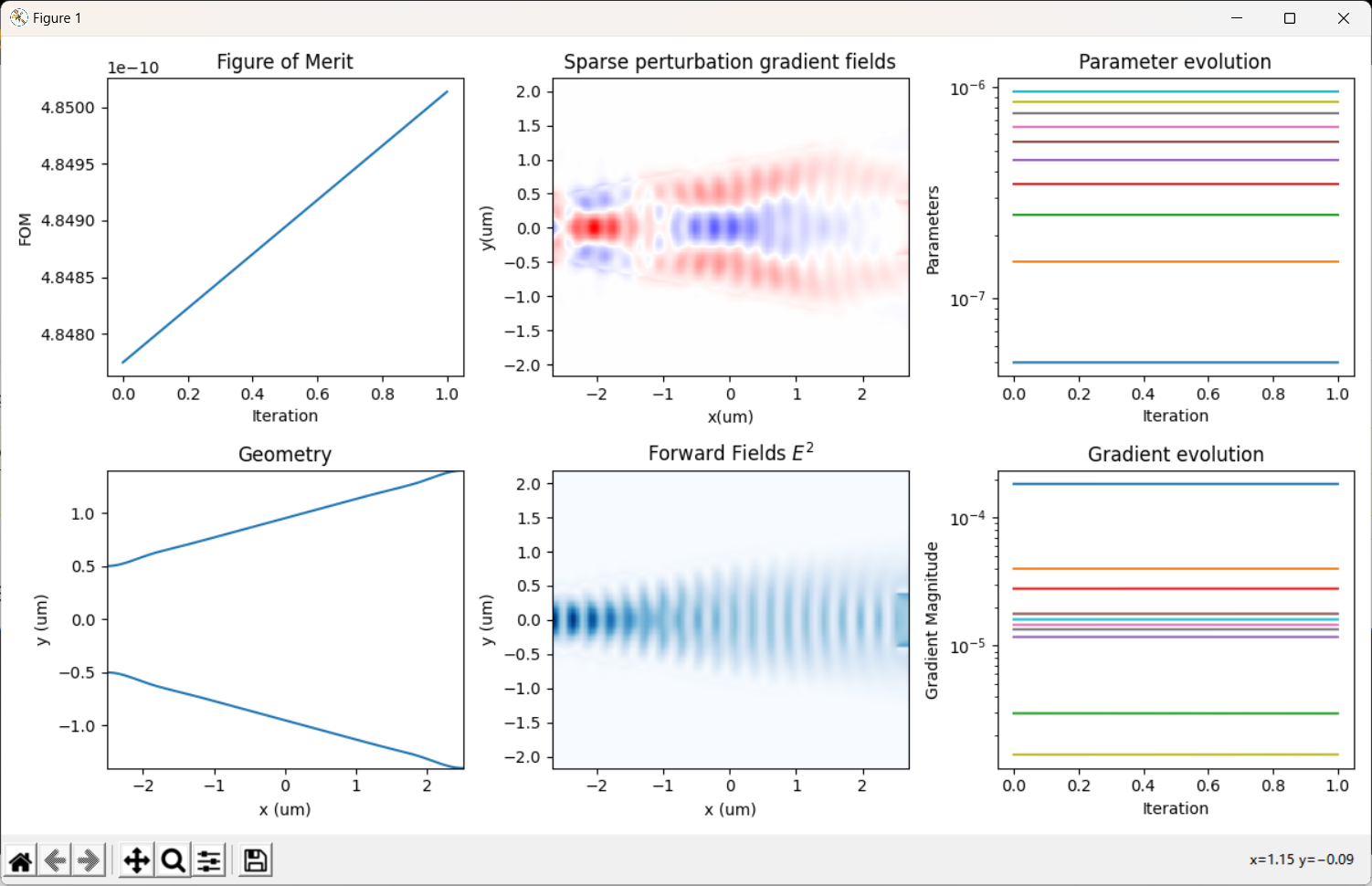
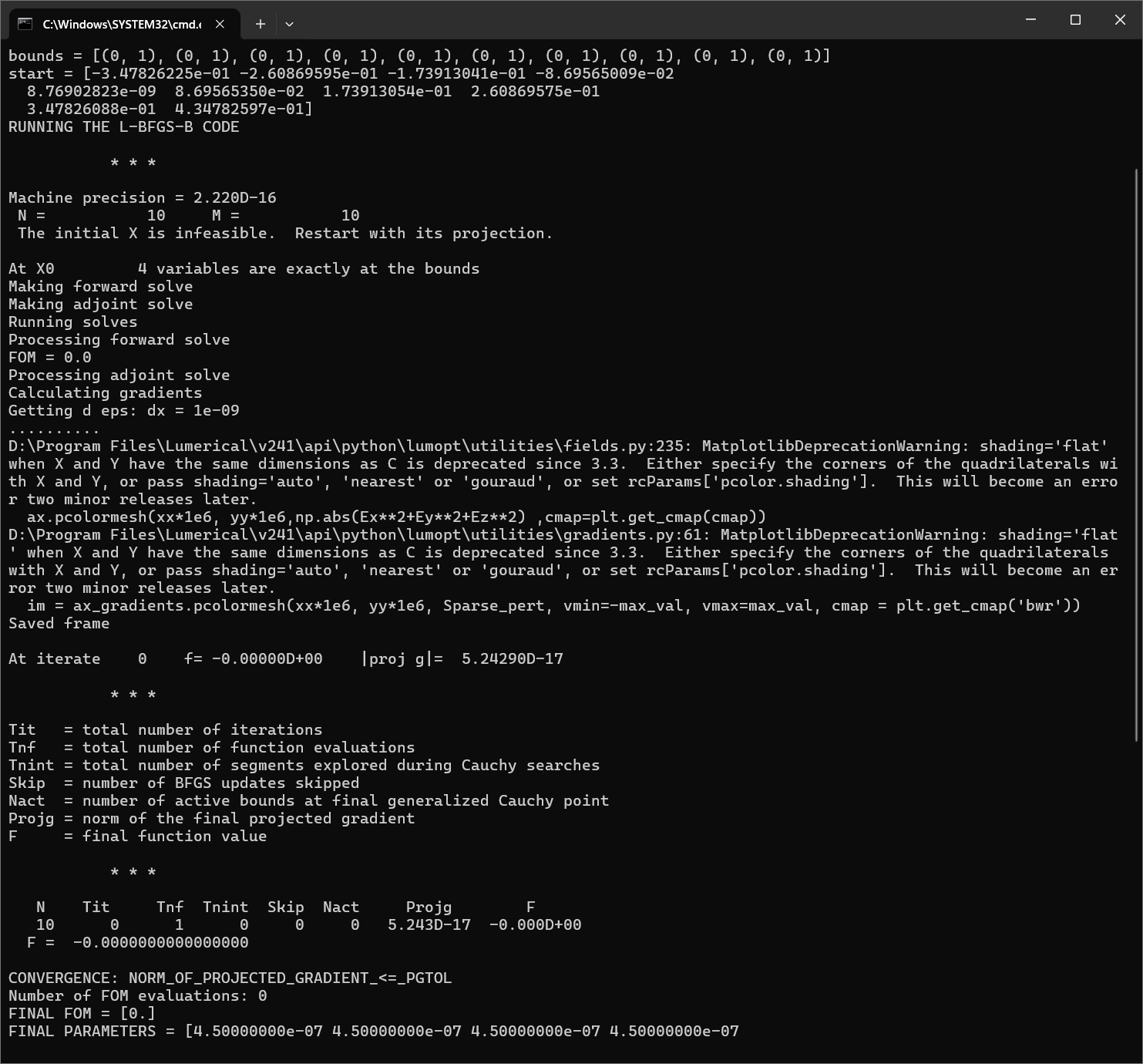
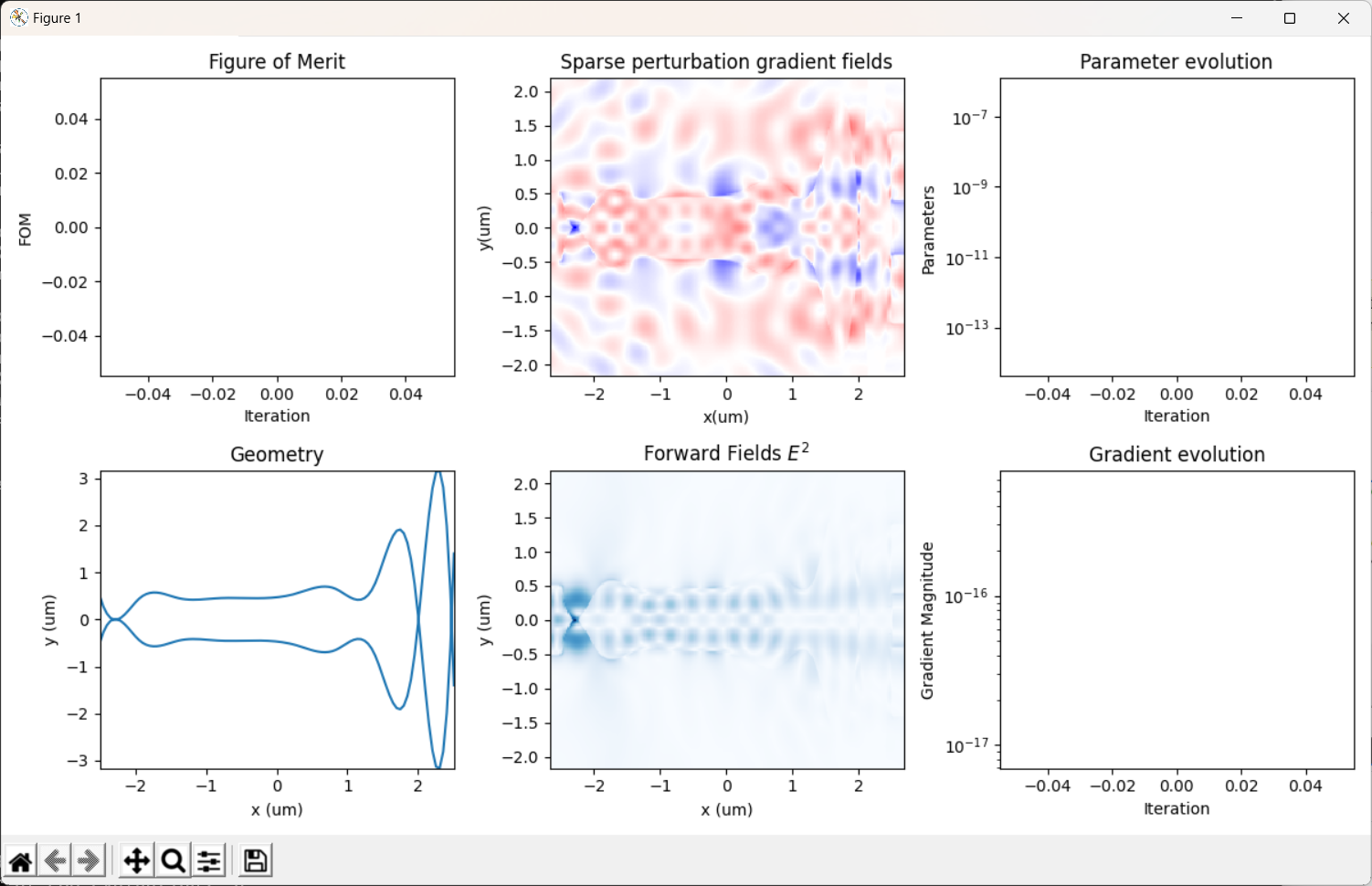
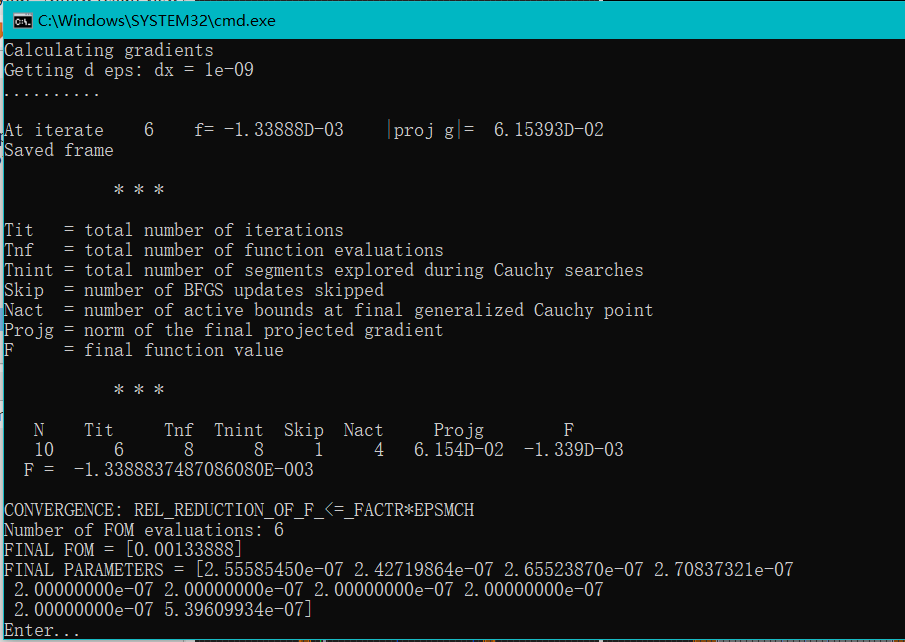
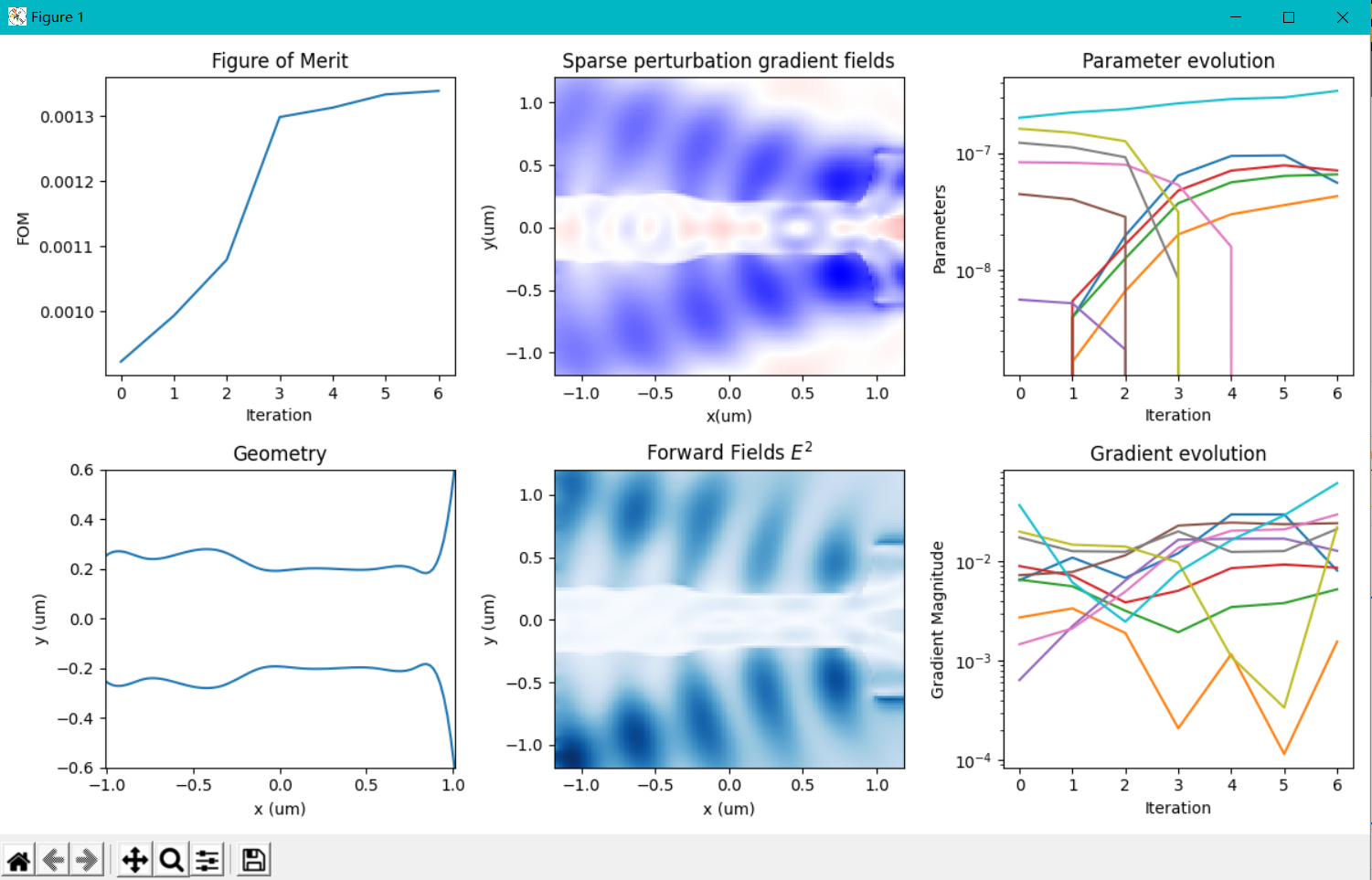
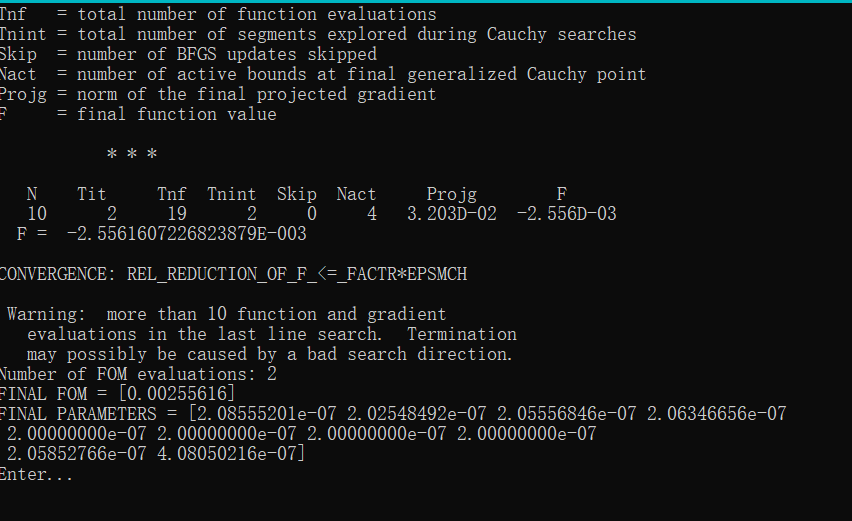
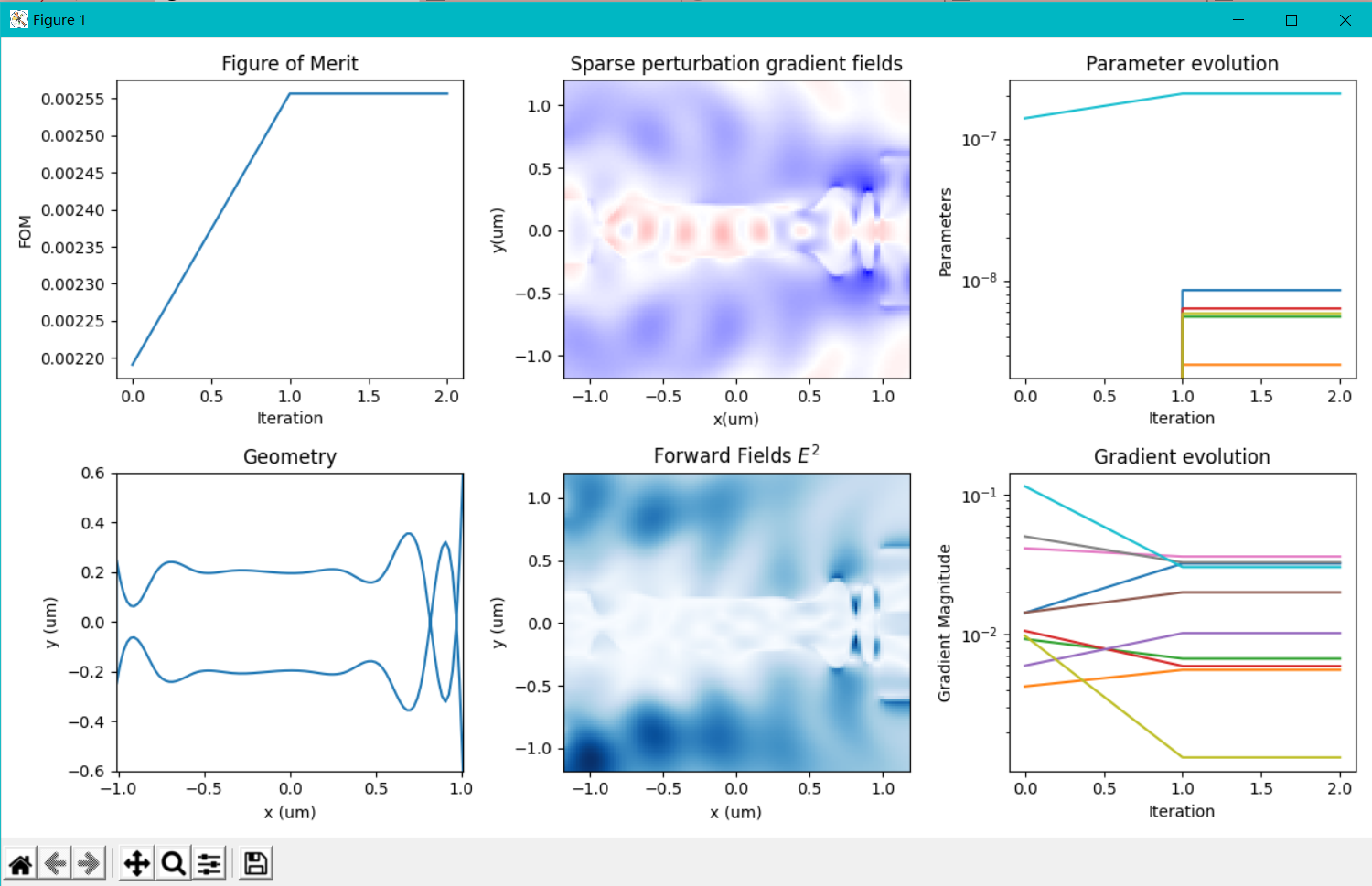
我在原案例代码的基础上进行了参数修改,更改了几何尺寸,即将输入、输出波导宽度改为1微米以便能激发出TE1模式,然后将中间的优化区域增大到大概5.5微米*4.5微米;并在优化python文件中,我也修改了相应的x,y坐标的范围以及bounds的范围;在选择输入模式光源的模式序号和输出fom的模式序号时,对于TE0模式,输入序号为2,输出选择3,对于TE1模式,输入选择4,输出选择8;并且边界条件为默认边界条件,没有采用对称边界条件,因为TE1模式不支持对称边界条件;其余设置均和案例中保持一致(具体代码在之前的提问中已经给出)。现在出现的问题是:当我按照上述设置进行优化时,对于TE0模式,fom的值非常小,在1e-10数量级,仿真在几代后便停止了,查看更新图像,发现参数并没有更新,意味着优化并未进行;对于TE1模式,优化在初始化完之后便停止了。具体截图如下
对于上述问题,我已经认真检查了代码,并没有发现错误,但为什么会出现这种情况就不是很明白了,还要麻烦老师予以解答,非常感谢!!
-
January 17, 2025 at 9:27 am
-
January 17, 2025 at 9:36 am
m202373352
Subscriber好的,还是非常感谢您的回复!
-
- You must be logged in to reply to this topic.



-
3407
-
1057
-
1051
-
896
-
882

© 2025 Copyright ANSYS, Inc. All rights reserved.