TAGGED: stress-concentration, stress-singularity
-
-
November 8, 2024 at 3:50 pm
gonthier
SubscriberDear all,
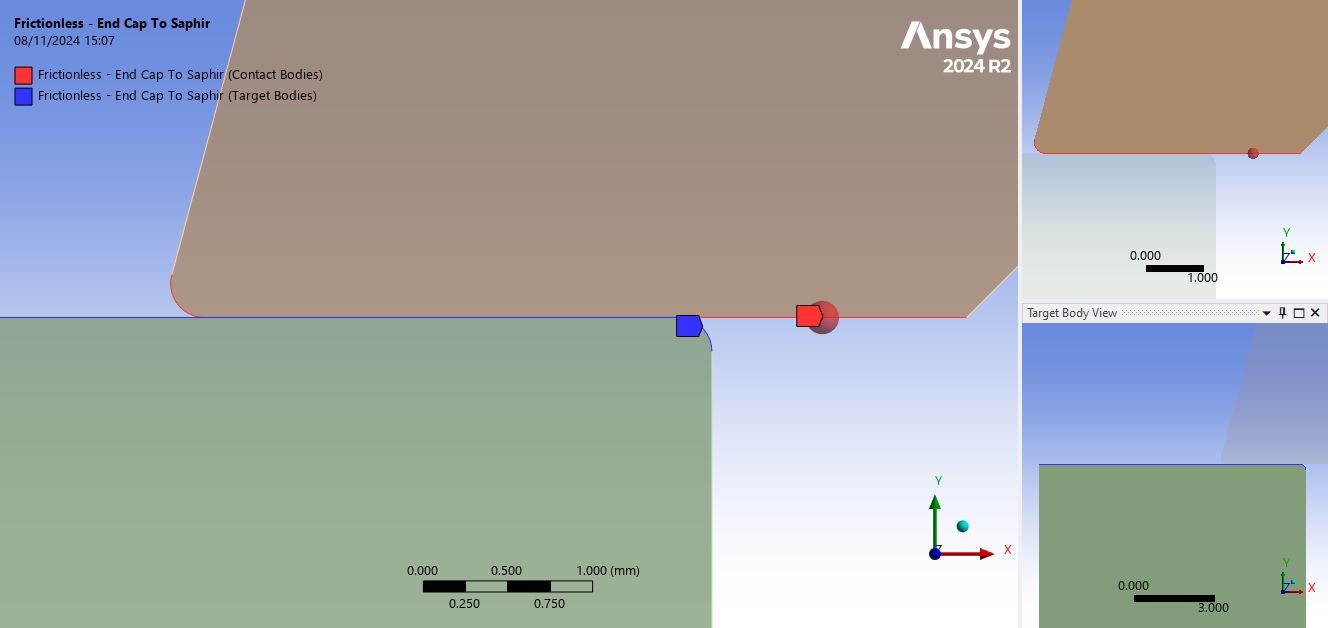
I am conducting a 2D static structural analysis of an optical window made of sapphire, which is in direct contact with a metallic component. The model is set up with axisymmetric 2D behaviour.
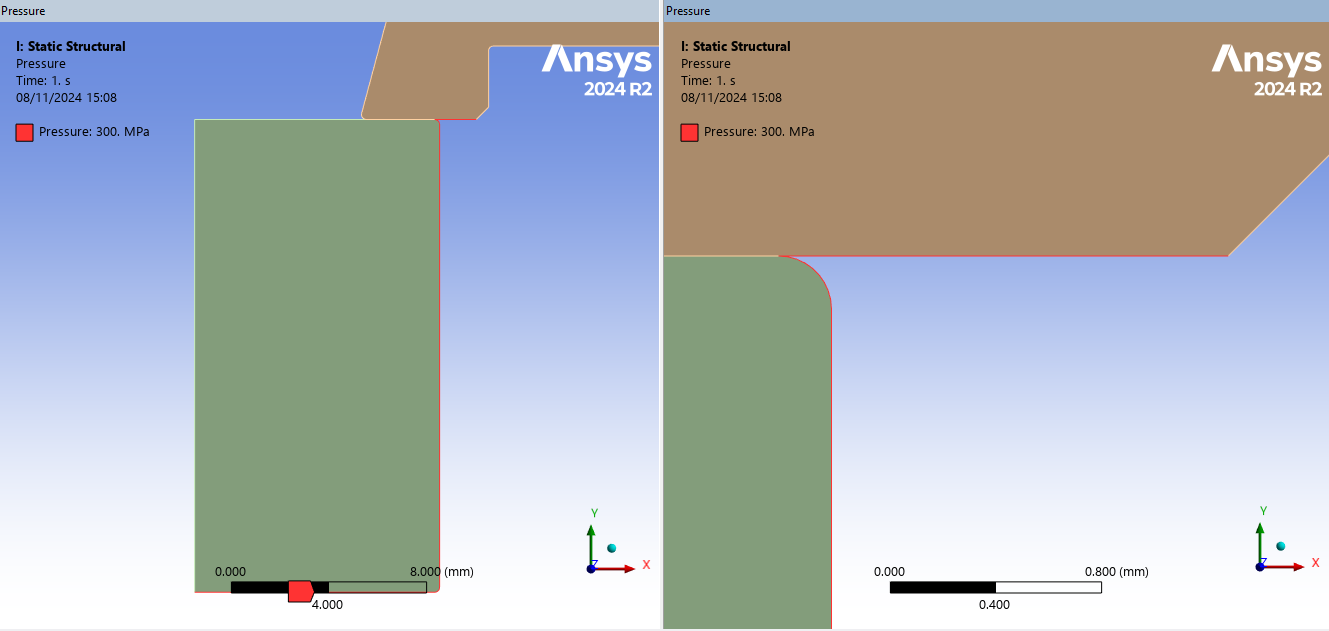
As shown in the attached screenshots, the mesh is refined (element size: 0.1 mm), the contact between the two parts is defined as frictionless, and pressure is applied on the red-highlighted surfaces. The optical window is cylindrical, with fillets around each flat surface.
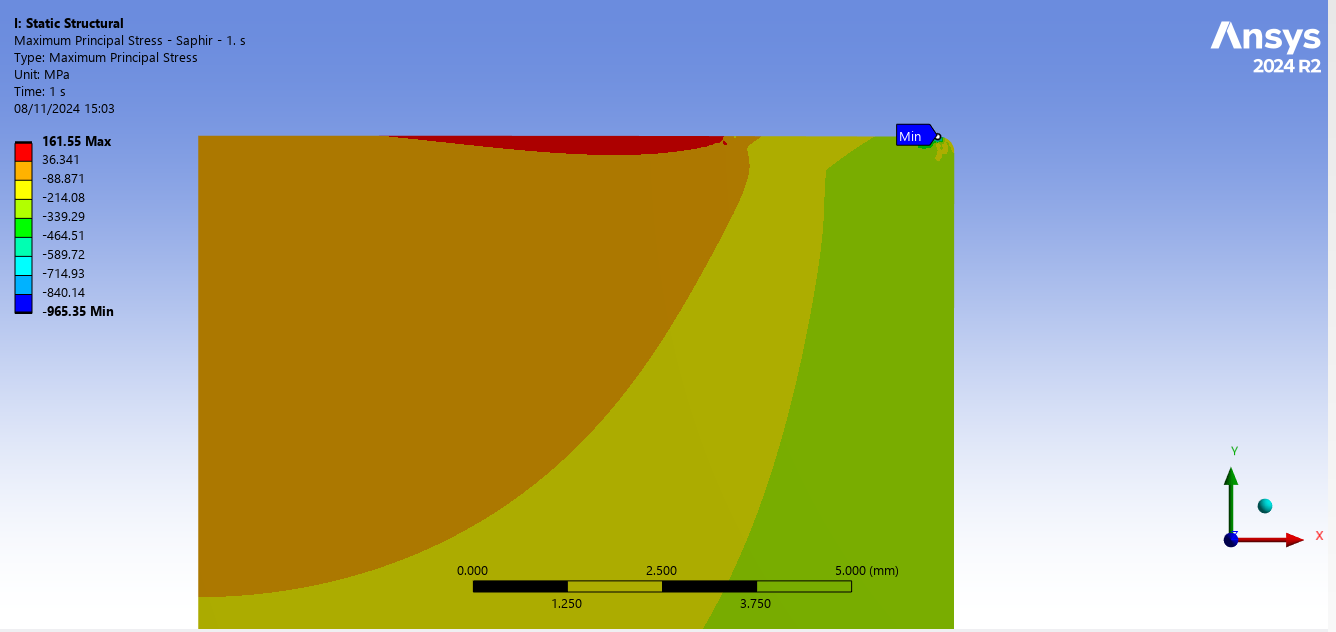
As expected, the maximum stress occurs at the base of the fillets. I suspect this is due to a geometric singularity, as the stress values increase when the mesh is refined. Despite my best efforts and research, I have not been able to mitigate this issue or obtain more accurate results.
Does anyone have suggestions on how to address this? Any advice would be greatly appreciated!
Thanking you in advance.
Julien -
November 11, 2024 at 2:13 pm
Daniel Shaw
Ansys EmployeeI recommend watching the video:
-
- You must be logged in to reply to this topic.



-
2979
-
970
-
857
-
750
-
599

© 2025 Copyright ANSYS, Inc. All rights reserved.