-
-
May 15, 2024 at 10:11 am
Jakob Heubner
SubscriberI'm trying to create a Tool in Ansys mechanical using the steady state thermal simulation, with which experimental data can be evaluated. The experiment contains a multiphase Fluid, which flows over a heated steel plate. During the experiments we want to measure the temperature at defined places inside the metal block and calculate the film coefficient from the temperature differences. Since Ansys mechanical needs the film coefficient for a convection boundary condition, I'm not sure how to implement this problem, due to the desired result being a required boundary condition.
I've thought about adding a APDL-Command with a surface temperature dependent heat flow (20°C leads to 0W,..,150°C leads to 200W) to emulate a convection. But with this approach the energy balance is not accounted for, which leads to my questions.
How can I define a temperature dependent heat flow with the condition that the accumulated heat flow is equal to the input heat flow?
Would the results of this approach be not only qualitatively but also quantifiable accurate?
Would using Ansys Fluent make the setup of this simulation simpler?
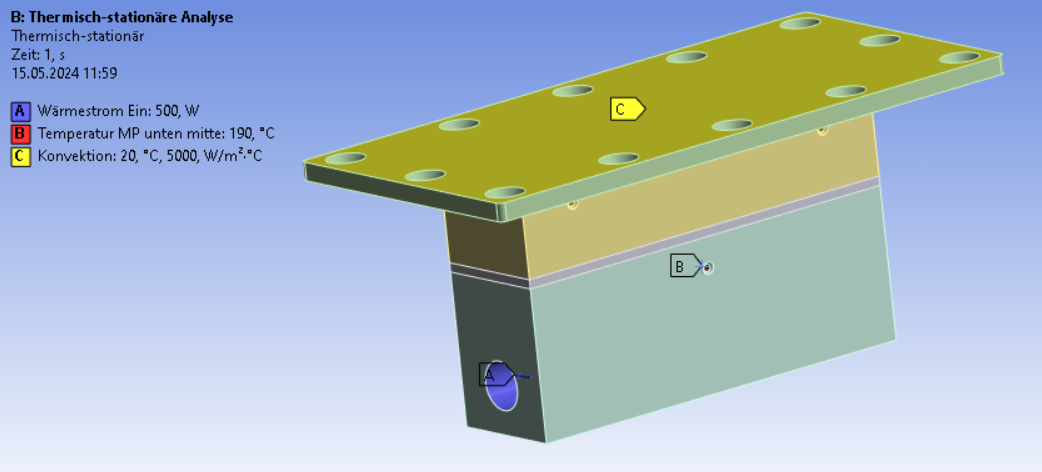
Attached is a picture of the geometry, where A is the induced heat flow and B is one of the temperature measure points and C is the area over which the fluid is flowing.
-
May 16, 2024 at 2:44 pm
dlooman
Ansys EmployeeA simplification can be to use an arbitrarily large value for tbulk so that "deltaT" doesn't affect the heat flow. Another simplification can be to convect to a thermal mass so that the change in enthalpy of the mass is a measure of total heat flow. These still don't seem to give you a way to control the total heat flow. Perhaps you could iterate on the solution in a *do loop. I'm not a Fluent user, but if the flow solution is already done, it doesn't seem any easier to use Fluent.
-
- The topic ‘Heat transfer simulation with convection film coefficient as a result’ is closed to new replies.



-
3487
-
1057
-
1051
-
955
-
922

© 2025 Copyright ANSYS, Inc. All rights reserved.