Tagged:
-
-
September 13, 2024 at 10:31 am
 FAQParticipant
FAQParticipant INTRODUCTIONThe Fluent GPU solver is a native GPU-powered solver, which uses graphics processing units (GPUs) to run complex CFD simulations. The Fluent GPU solver is available starting in version 2023 R1 and onwards.
INTRODUCTIONThe Fluent GPU solver is a native GPU-powered solver, which uses graphics processing units (GPUs) to run complex CFD simulations. The Fluent GPU solver is available starting in version 2023 R1 and onwards. Table of Contents
Table of ContentsFAQs
- Which license is required to run Fluent on GPUs?
- Which GPU cards are recommended for use with Fluent?
- What if I don’t have access to NVIDIA or AMD GPU Cards?
- What kind of performance gains can I expect to see?
- Are there any benchmarking studies?
- What types of simulations can currently be run on the GPU Solver?
- What types of industries can benefit the most from GPU Solvers?
- Where can I learn more?
APPENDIX
1. What are streaming multiprocessors (SMs) and compute units (CUs)?
 FAQs
FAQs1. Which license is required to run Fluent on GPUs?
In order to run Fluent on GPUs, you need a license that provides access to:
- CFD Enterprise capabilities version 2023 R1 or later, or
- CFD HPC Ultimate 2025 R1 SP1 or later.
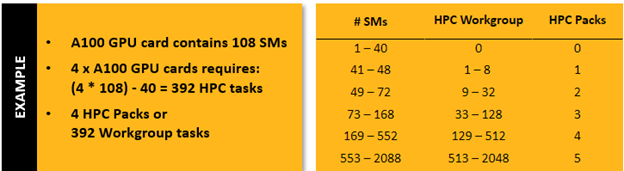
CFD Enterprise Licensing is based on the total number of streaming multiprocessors (SMs), if using NVIDIA GPUs, or compute units (CUs) if using AMD GPUs. 40 SMs/CUs are included with the CFD Enterprise license. For additional SMs/CUs with CFD Enterprise you must purchase Ansys HPC licenses. See the appendix for additional information about SMs/CUs.
The CFD HPC Ultimate enables unlimited SMs/CUs without the need for additional HPC licenses. To determine which license is the best fit for you, contact your Ansys Account Representative.
2. Which GPU cards are recommended for use with Fluent?
The Fluent GPU Solver is written on an Ansys proprietary GPU architecture that supports AMD GPUs (Beta in 2024 R1, full support with 2024 R2) and NVIDIA GPUs.
Supported NVIDIA GPUs include the NVIDIA Tesla and Quadro series, as well as GPUs listed on the Platform Support section of the Ansys Website.
Supported AMD GPUs include the MI210, MI250, MI250X, MI300A and MI300X. For NVIDIA GPUs, your GPU driver must be compatible with CUDA version 11.0 or newer.
General Hardware recommendations can also be found on the Ansys Customer Portal.
3. It’s difficult to purchase GPU cards right now, what if I don’t have access to GPU Cards?
The large memory Server GPUs (A100, H100, MI300) are in high demand for AI/ML applications. However, L40 GPUs are easily available and two of these can have a similar performance to a single A100 at a significantly lower hardware cost. Alternatively, cloud providers now can give customers access to high end GPUs. These are both solutions that we have used internally at Ansys to support the development of the GPU solver.
4. What kind of performance gains can I expect to see running Fluent on GPUs?
Comparing GPUs and CPUs is not an apples-to-apples comparison, and the performance gains are of course heavily dependent on the GPU hardware and CPU hardware used in the comparison. But it is still helpful to draw such comparisons.
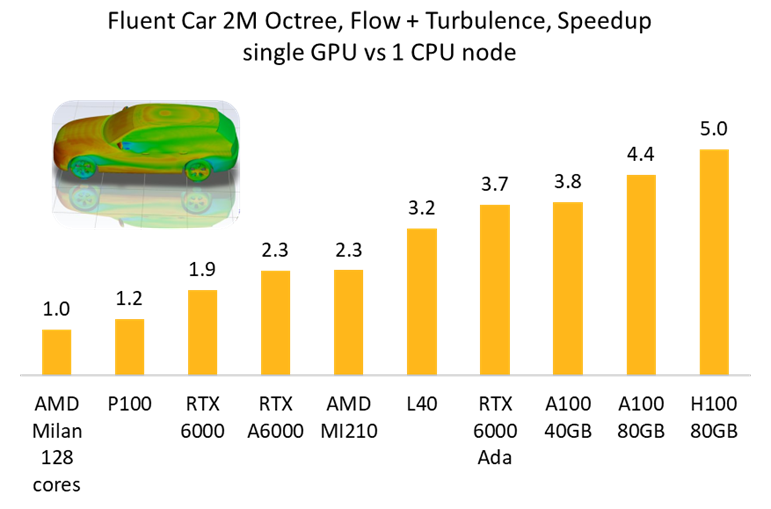
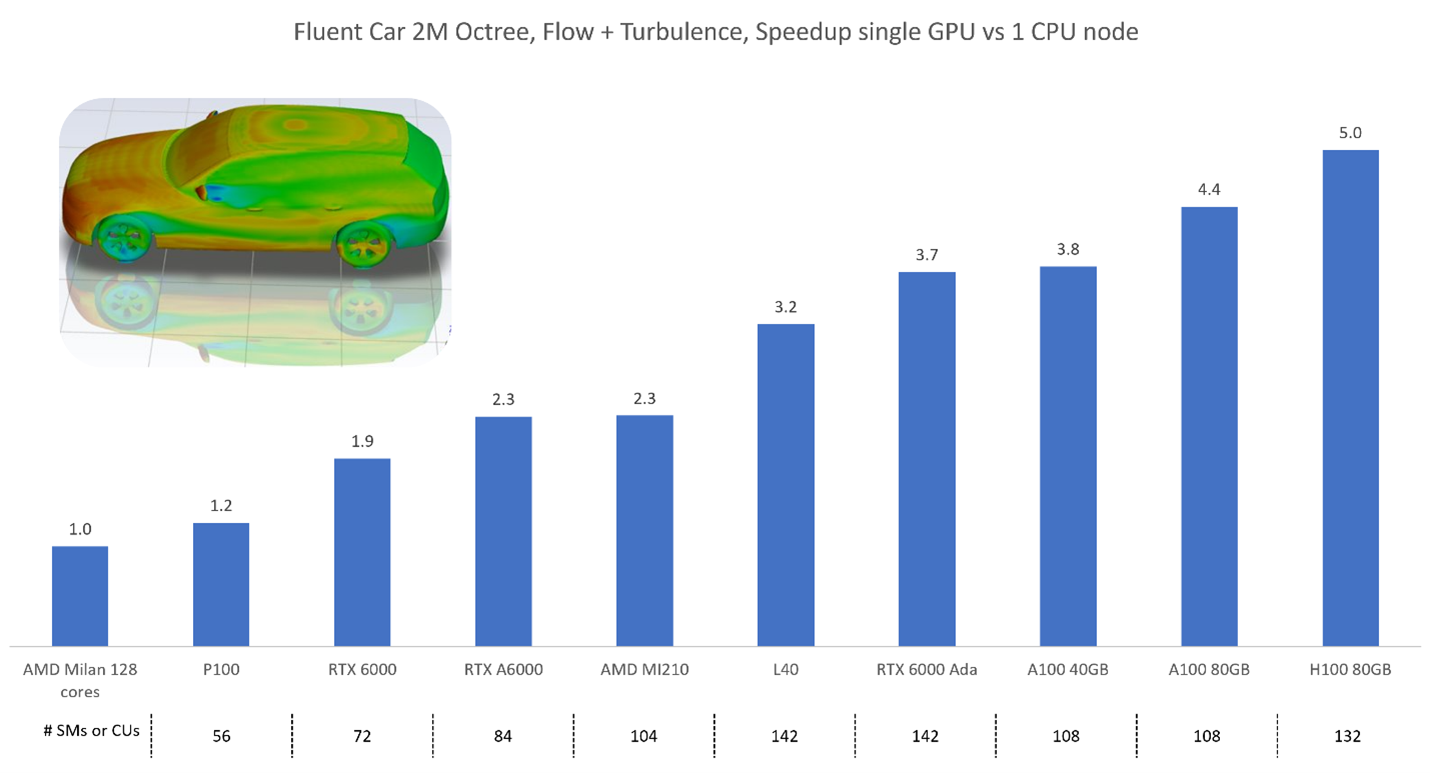
From our single-GPU benchmark studies, we have seen that the performance of 1 recently released GPU ranges from 200-500+ CPU cores, depending on if it is a laptop/desktop card or a server card.
In the below example, we saw a 5X speed up using a NVIDIA H100 80GB GPU compared to an AMD Milan 128 core CPU system. This implies that a single H100 is equivalent to 640 CPUs.
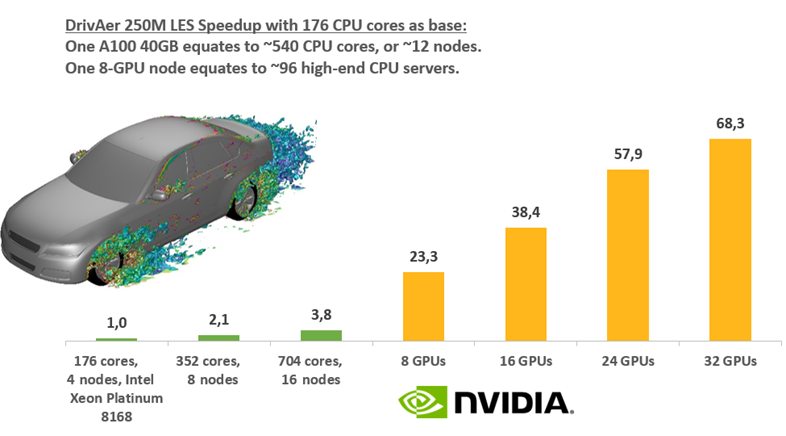
We have similar metrics when comparing multi-GPU performance benchmarks. In the example below, we see that running a 250M cell LES model on 8 A100 (40GB) cards gives 23.3X speedup compared to 176 cores. This implies that 1 GPU is equivalent to 512 cores.5. How accurate is Fluent’s GPU Solver? Are there any benchmark studies?
Yes, there are several whitepapers and publications available that showcase internal testing we have performed on canonical cases, including laminar flow cases and turbulent flow cases to validate code accuracy. You can access these here:
- CFD Validation Studies and Accuracy Improvements in Version 2024 R2
- Automotive CFD Prediction Workshop
For GPU Solver speed benchmarking, you can access the below resources:
To conduct performance benchmarks on your own system, we have a variety of cases available specifically for the GPU solver. Scroll down at this link:
https://support.ansys.com/TrainingAndSupport/ANSYSFluentBenchmarks
You may also request a custom benchmark below:
Ansys Multiphysics Benchmarking Program
6. What features and capabilities are currently supported on the Fluent GPU solver?
The following is supported on the GPU Solver at 25 R1:
- Single/multi- GPU (shared/distributed memory)
- CPU/GPU re-mapping (invoke with –gpu_remap)
- Low speed compressible solver
- Steady and transient simulations
- Segregated and coupled solvers
- Species transport
- EDM combustion model
- Stiff Chemistry Solver
- Adiabatic and non-adiabatic Flamelet Generated Manifold (FGM) model
- Acoustics with Ffowcs Williams & Hawking (FW-H)
- Surface-to-Surface (S2S) radiation model
- DO radiation model
- Discrete Phase Model (DPM) (b)
- Ideal gas and viscous heating
- Volume of Fluid (VOF) method (b)
- Incompressible and compressible flows
- All mesh types
- Ideal Gas and Materials with variable properties
- Turbulence: laminar, standard and realizable (RKE) k-espilon, k-omega SST, GEKO, SBES, LES, Gamma-Algebraic Transition Model
- Solid conduction and conjugate heat transfer (CHT), with anisotropic conductivity
- Extended monitors – Asynchronous monitors, point/cut plane monitors, mass averages and sum
- Porous media
- Parametric workflow
- Windows and Linux
For more detailed information, visit the Ansys Help Site.
7. What types of industries can benefit the most from GPU Solvers?
The GPU solver is a general-purpose solver that, like Fluent’s traditional CPU solver, benefits all industries. The major industries where it can benefit are the same as Fluent’s CPU solver: A&D, auto and ground transportation, high tech, and chemical/material processing. While at 24R1 it does not yet cover all of the physics of Fluent’s CPU solver, there are use cases with each of these industries where the GPU solver provides major benefits.
8. Where can I learn more?
Ansys Help Documentation provides additional information and details about the GPU Solver, including tutorials, limitations, trouble shooting and more.
- Chapter 36: Using the Fluent Native GPU Solver (ansys.com)
- Ansys Innovation Courses: Getting Started with Fluent GPU Solver
 APPENDIXHPC Requirements for Common GPUs using a CFD Enterprise**Assuming 1.2GB GPU RAM per million cells for a typical Single precision Steady State SIMPLE model. Actual GPU RAM requirements per million cells will be case specific and will depend on the mesh type, physics solved, single vs. double precision and other factors. Double precision and the Coupled solver significantly increase RAM requirements. Larger mesh sizes can be solved using multiple GPUs.
APPENDIXHPC Requirements for Common GPUs using a CFD Enterprise**Assuming 1.2GB GPU RAM per million cells for a typical Single precision Steady State SIMPLE model. Actual GPU RAM requirements per million cells will be case specific and will depend on the mesh type, physics solved, single vs. double precision and other factors. Double precision and the Coupled solver significantly increase RAM requirements. Larger mesh sizes can be solved using multiple GPUs.
Example of HPC Packs required with CFD Enterprise for an NVIDIA A100 GPU Card1. What are streaming multiprocessors (SMs) and compute units (CUs)?
A SM or CU is a fundamental component of a GPU card, with nomenclature that is vendor dependent. NVIDIA GPUs are comprised of streaming SMs that contain CUDA cores, and AMD GPUs are comprised of CUs that contain stream processors. A SM/CU is a collection of processing units that work together to execute command kernels (CUDA for NVIDIA, HIP for AMD). Each SM/CU consists of several smaller cores, which are responsible for executing parallel computations and performing tasks related to rendering and other general-purpose computing.
The number of SMs/CUs in a GPU depends on the specific model and architecture. For example, the NVIDIA GeForce RTX 3080 has 68 SMs, while the NVIDIA Tesla V100 has 80 SMs. Similarly, the AMD MI210 contains 104 CUs. More powerful GPU cards typically contain more SMs/CUs.
-


Introducing Ansys Electronics Desktop on Ansys Cloud
The Watch & Learn video article provides an overview of cloud computing from Electronics Desktop and details the product licenses and subscriptions to ANSYS Cloud Service that are...

How to Create a Reflector for a Center High-Mounted Stop Lamp (CHMSL)
This video article demonstrates how to create a reflector for a center high-mounted stop lamp. Optical Part design in Ansys SPEOS enables the design and validation of multiple...

Introducing the GEKO Turbulence Model in Ansys Fluent
The GEKO (GEneralized K-Omega) turbulence model offers a flexible, robust, general-purpose approach to RANS turbulence modeling. Introducing 2 videos: Part 1 provides background information on the model and a...

Postprocessing on Ansys EnSight
This video demonstrates exporting data from Fluent in EnSight Case Gold format, and it reviews the basic postprocessing capabilities of EnSight.

- How to overcome the model information incompatible with incoming mesh error?
- Ansys Fluent GPU Solver FAQs
- Is there a way to get the volume of a register using expression ?
- Skewness in ANSYS Meshing
- What are the requirements for an axisymmetric analysis?
- How to create and execute a FLUENT journal file?
- What are pressure-based solver vs. density-based solver in FLUENT?
- How to get information about mesh cell count and cell types in Fluent?
- What is a .wbpz file and how can I use it?
- How can I Export and import boxes / Systems from one Workbench Project to another?

© 2025 Copyright ANSYS, Inc. All rights reserved.