-
-
October 23, 2024 at 11:57 am
Nese.Halilbese
SubscriberHi;
I want to simulate the heave motion of two nested cylinders. While I'm able to obtain results from the Hydrodynamic Diffraction analysis, I’m having trouble getting the Hydrodynamic Response in a Regular Wave simulation. What could be the issue?"
My second question is: if the inner cylinder (closed) were below the water level, would I be able to model it? Is it possible to observe heave motion for structures that are submerged below the water surface?
-
October 23, 2024 at 5:01 pm
Shuangxing Du
Ansys EmployeeI may assume that in your model the external surface is meshed only for the external cyliner. The cylindral surface of the internal cylinder should be modelled as non-diffraction panels and only the bottom surface could be modelled as diffraction surface if this surface is submerged.
In Hydrodynamic time domain response analysis, the relative motions between the hydrodynamic interation structures should be small. If the motions are big, could you please consider to add in some constraints, such as fenders to reduce the translational motions between two structures and to define larger moment of inertia about cylinder axis for the cylinders to reduce the yaw rotations?
The inner cylinder (closed) being below the water level is allowed. If it is totally submerged, you may need to set it as a sumberged structure. As there is no hydrostatic stiffness for a fully submerged structure, please check if you need to define some structural stiffness such as moorings/fenders to keep this structure in the desired mean location. The heave motion of a fully submerged structure can be observed by either animation or plotting structure position in Z direction.
-
October 24, 2024 at 10:50 am
Nese.Halilbese
SubscriberThank you so much for your responce.
I have a submerged piston inside the cylinder. As you suggested I tried to define fenders the keep the piston inside the cylinder. I have two component one is piston, and the other one is cylinder. The cylinder's inner radious is R1=50 mm, and piston's radious is R2=48 mm. Piston's top surface distance to the waterline is H1=155 mm, and Piston's bottom surface distance to the waterline is H2=175 mm.
I defined 8 connection point for each component to define fenders.For cylinder they are: (R1,0,-H1),(0,R1,-H1),(-R1,0,-H1),(0,R1,-H1), and for the piston they are:(R2,0,-H1),(0,R2,-H1),(-R2,0,-H1),(0,R2,-H1). These are for the top side I also did the some thing for the bottom side with H2.
1-Are they should be floating fender or fixed?Can I define the distance between piston and cylinder like 2 mm. Is this gap to small?
2-To get result from Hydrodynamic Diffraction I had the delete one of the inner surface. If I dont delete the surface , I had to divide into two component and use to joint. But with joint, I guess I had another problem during the Hydrodynamic responce so this time I just delete it.
3- Should I define Interracting structure groups to get result in Hydrodynamic responce.
4-Diactivated freedom for both structure on X,Y,RX,RY. Regular wave is defined. What is missing?
Thanks for your time and effort.
-
October 24, 2024 at 11:59 am
Shuangxing Du
Ansys Employee1-Are they should be floating fender or fixed?Can I define the distance between piston and cylinder like 2 mm. Is this gap to small?
They should be fixed fenders. It will be good to define the fixed point (on the external cylinder) away from the internal surface of that cylinder, in order to make the size of the fender to be larger than 2mm to avoid the error shown in the error message of "ZERO/NEAR ZERO SIZE ...". Normally the size (not less than the initial distance between the fixed point to the contacting surface) should be greater than 0.001*G, where G is the acceleration due to gravity.
2-To get result from Hydrodynamic Diffraction I had the delete one of the inner surface. If I dont delete the surface , I had to divide into two component and use to joint. But with joint, I guess I had another problem during the Hydrodynamic responce so this time I just delete it.
The inner surface may not be neccessary to be deleted, instead you can define the surface as non-diffracting and set this surface and the bottom surface in a single part.
3- Should I define Interracting structure groups to get result in Hydrodynamic responce.
As the relative motion between piston and the external cylinder is large, it may be good if you can avoid them to be in the same hydrodynamic interaction group.
4-Diactivated freedom for both structure on X,Y,RX,RY. Regular wave is defined. What is missing?
As the fenders are defined in two horizontal levels, there is no need to deactivate freedoms of X,Y, Rx, Ry. But do you need to find mooring lines (or connectin joint to the fixed point) to keep the external cylinder to the desired position?
-
October 24, 2024 at 12:45 pm
Nese.Halilbese
SubscriberThank you so much,
I suspress the fenders.I got results like;
for the cylinder
for the piston;
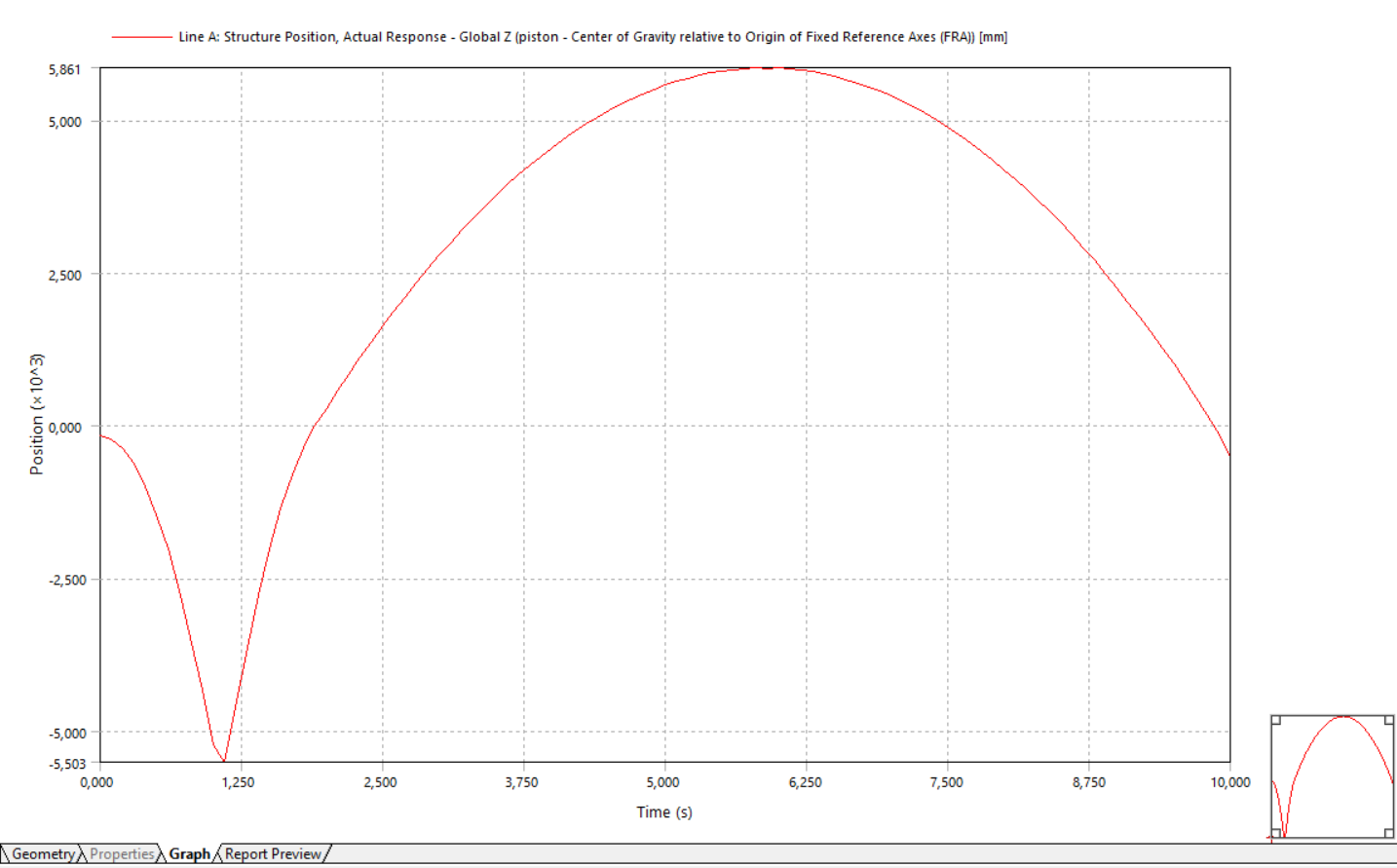
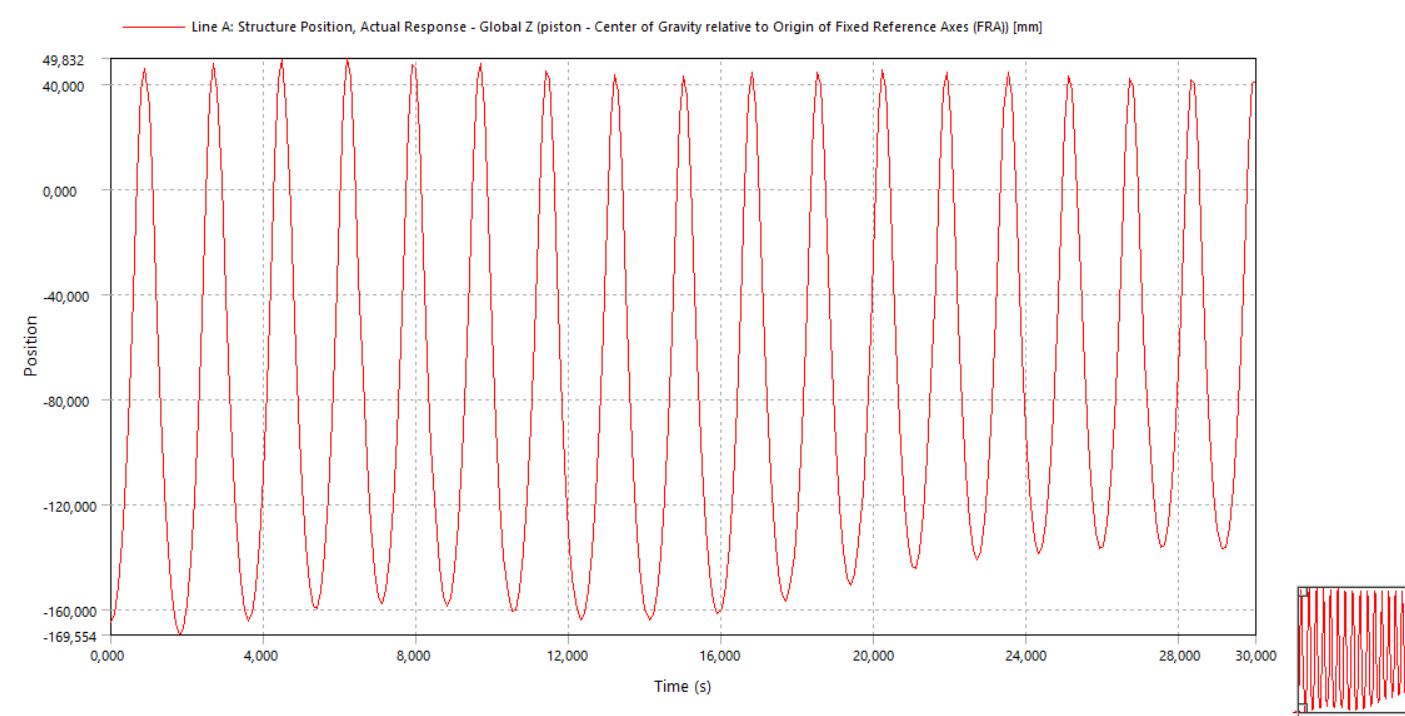
I think the result is correct for the cylinder but for the piston its not. I dont want to use mooring lines because in the actual model there is no mooring lines. In the actual model, the piston is located inside the cylinder and it moves up and down by itself with different speed. What I am trying the show is the cylinder and piston will move with different speed.
-
October 24, 2024 at 1:05 pm
Shuangxing Du
Ansys EmployeeWithout mooring lines and/or other constraints, I guess the whole system is freely floating. From your results, the cyliner's COG z-position is in the range of (-76, -65) mm. But the piston's cog position is in range of (-5200, -1800) mm. Is it what you expect? What is the length of the piston?
-
October 24, 2024 at 3:05 pm
Nese.Halilbese
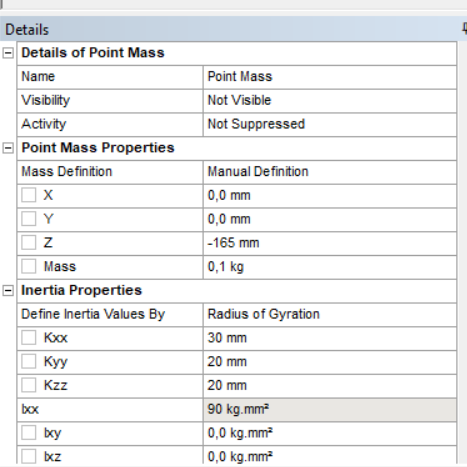
SubscriberYes, the whole system is freely floating. No, Its not what I expect for the position of the piston. The mass center of the piston is (0,0,165 mm), the height of the piston is 20 mm, diameter is 96 mm. When I only model the piston with the same location (submerged) I got meaningless position. Time step is 0,001 s, and I diactivated RotZ
-
October 25, 2024 at 8:44 am
Shuangxing Du
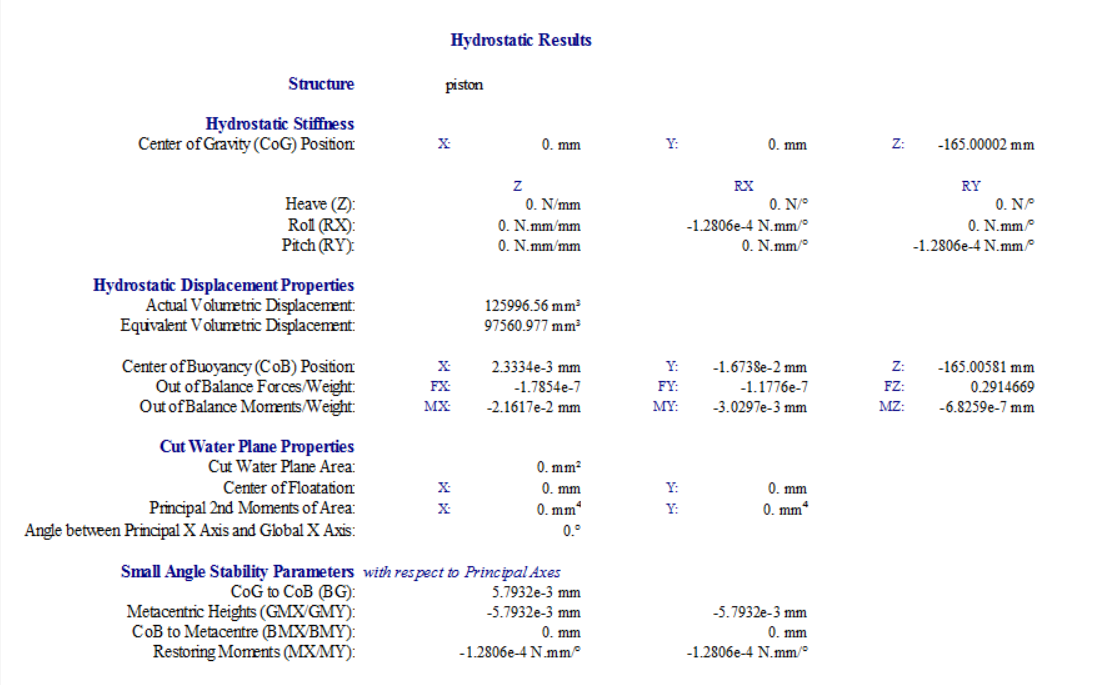
Ansys EmployeePlease check all the force components (such as, Froude-Krylov force, hydrostatic force, etc) in z direction. One or more force components may not be right in your model. From z-poistion time history, within the starting one second time, the piston drops down by 5 meters, which may mean that the piston motion is mainly freely falling due to the gravity force, the hydrostatic force is either small or in the wrong direction. If the hydrostatic force is either small or in the wrong direction, please check the surface normal direction of the piston. Aqwa requires all the surfaces'normal directions point towards external fluid region.
-
October 25, 2024 at 9:34 am
-
October 25, 2024 at 9:58 am
-
October 25, 2024 at 1:43 pm
Shuangxing Du
Ansys EmployeePlease check the force components, you may see what unrealistic force(s) cause the problem.
-
November 7, 2024 at 2:43 pm
Nese.Halilbese
SubscriberDear Shuangxing Du;
For analyzing the hydrodynamic response of the piston:
The piston’s point mass is positioned at -665 mm. A regular wave was defined with an amplitude of 1 mm, a frequency of 10 rad/s, and a wavelength of 616.16 mm. According to theory, the wave effect should reach a depth equal to half the wavelength.
However, the piston is not remaining stable underwater. What could be causing this instability? By the way, the water depth is 70000 mm.
-
November 7, 2024 at 4:07 pm
-
- You must be logged in to reply to this topic.



-
4929
-
1623
-
1386
-
1242
-
1021

© 2026 Copyright ANSYS, Inc. All rights reserved.