TAGGED: c-vof, courant-number, fluent, transient
-
-
July 17, 2024 at 2:48 pm
Dato
SubscriberHi everyone,
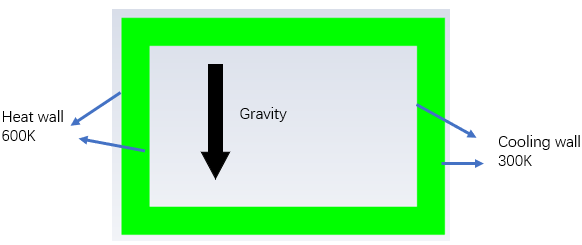
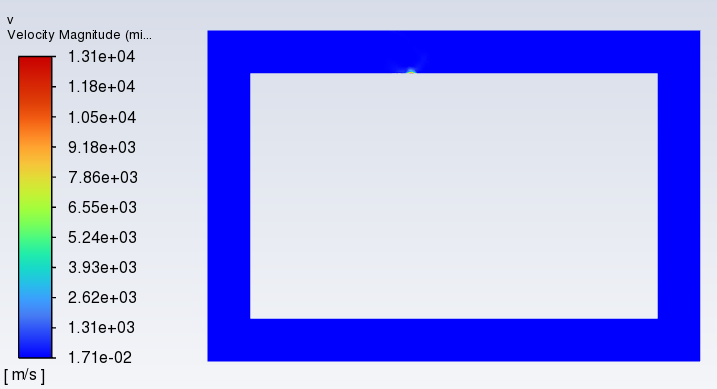
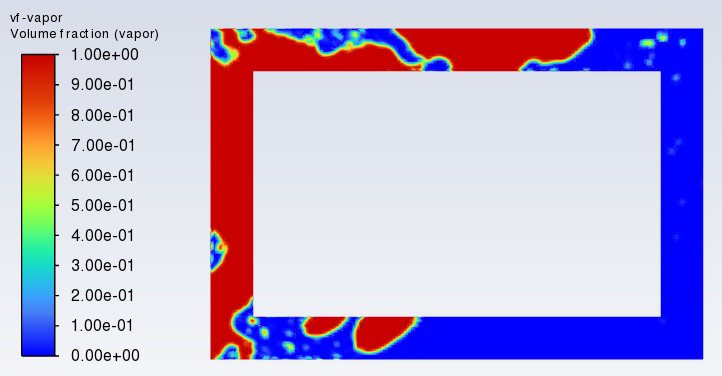
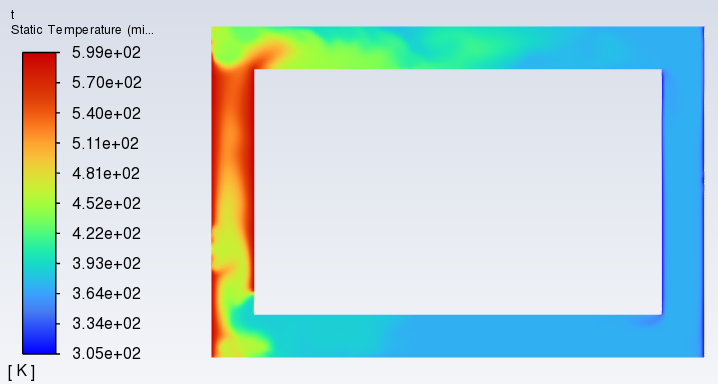
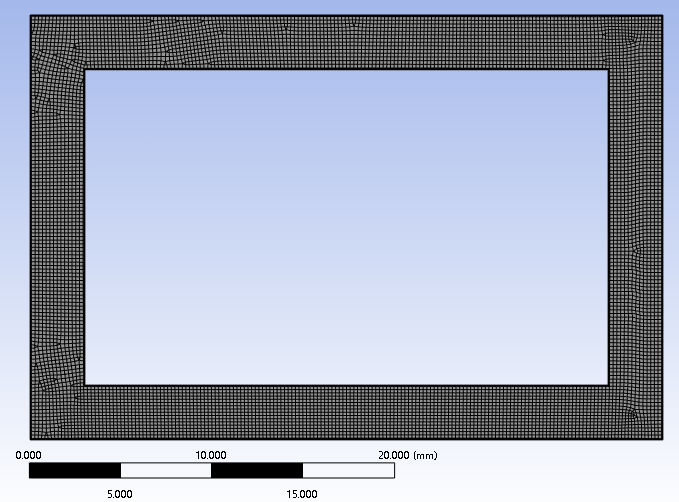
I'm a freshman doing transient simulation. I'm doing 2D tranient natural circulation simulation using VOF model. In the case, Water will be heated and generated vapor to drive the circulation. Model is shown below.
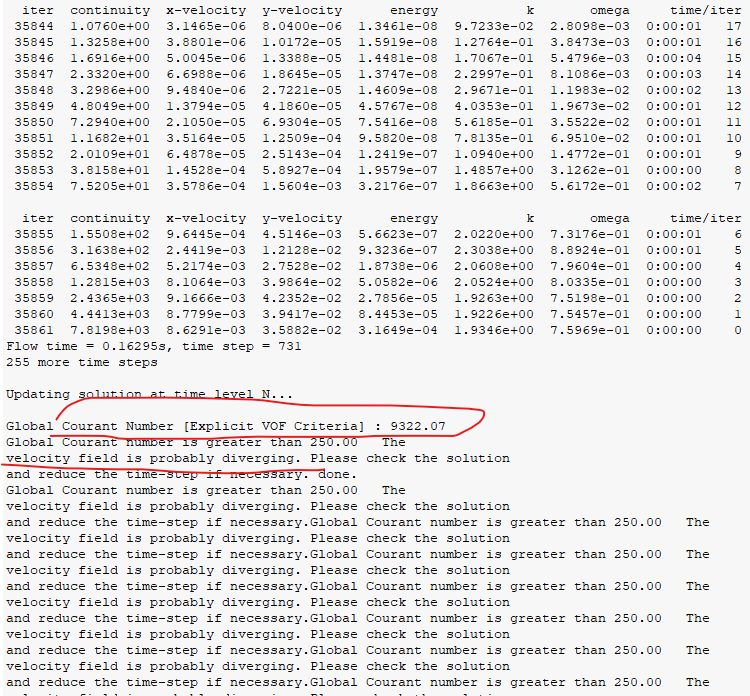
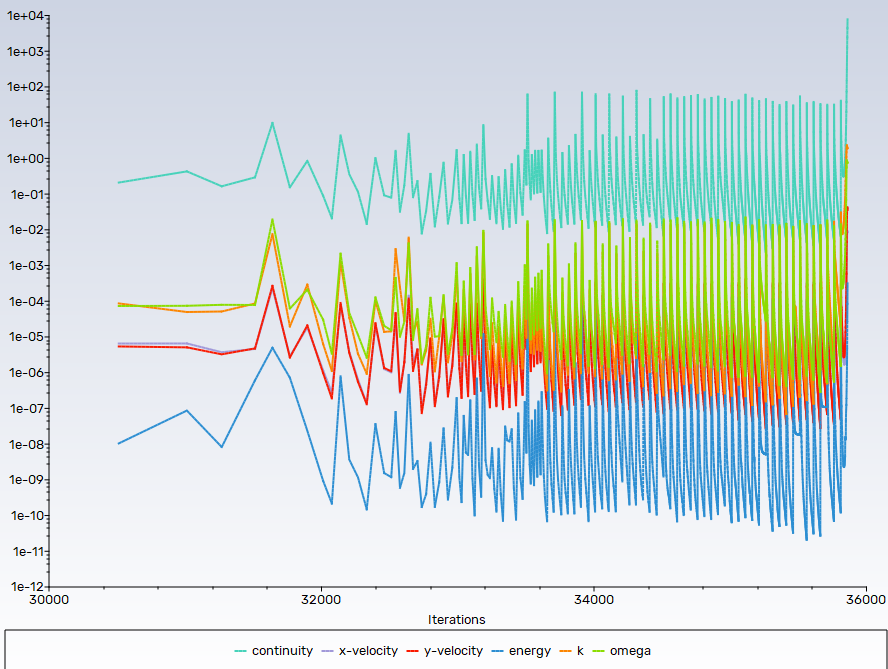
Firstly, solution converge and contour seemed reasonable. However, solution suddenly diverged with global courant number surged to 9322.7.
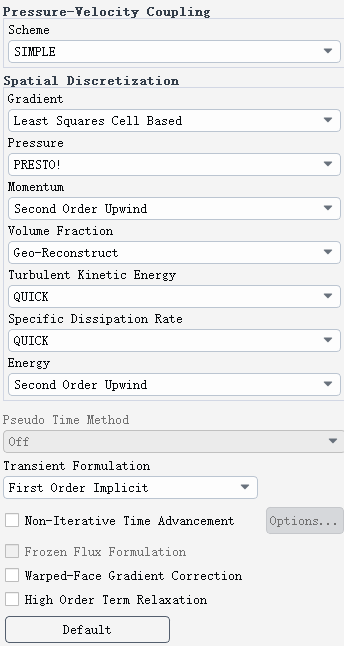
Discretization scheme and residual and console is shown below.
messages shown indicates that velocity field is abnormal and it did. Below velocity, volume fraction of vapor and at last time step.
I really have no idea that I have encountered the siuation when I run it again.
I'm using Lee model and parameters used in the model is by default. Fixed e-4 time step is set.
I'm really confused by the sudden ascending courant number and abrupt divergence. Any kind of suggestions would do me a great help
-
July 18, 2024 at 11:22 am
Rob
Forum ModeratorHow are you modelling the vapour density? How big is the domain?
-
July 19, 2024 at 4:14 am
Dato
SubscriberSorry that I'm not exactly understand what "modelling the vapour density" means. Initially, It fills with water and constant wall temperature is applied. I heard Rayleigh number should be evaluated but I ignore it and k-epsilon model is applied.
Dimension of calculation domian is shown below. Boundary layer cells are considered.
I have another question: when using Multiphase models like VOF or RPI model, whether near-wall mesh should be placed in turbulence fully developed region, while I always have Y+=1 in single phase flow to use visous sublayer resolved method.
-
-
July 19, 2024 at 10:29 am
Rob
Forum ModeratorRead the background for wall boiling models: you don't want to overrefine the near wall region. The other problem you've got now is the cell aspect ratio. Inflation is great for aero type models with no change in the streamwise gradients, they're a liability in multiphase as they're just a very high aspect ratio cell in precisely the wrong place.
Now, if your domain is initially full of water, and you boil that. Where does the volume go/come from in the model? In reality you may compress something or deform the casing, in CFD if you've not set material properties it's not going to do what you expect.
-
July 19, 2024 at 12:21 pm
Dato
SubscriberDear Dr Rob,
Water-liquid density is specified as temperature dependent but density of water-vapor is a constant. Oh, it's said that density of water-vapor must be set as real gas or something. Otherwise it's not conform to reality and hence solver may encounter numerical problems. Is it right?
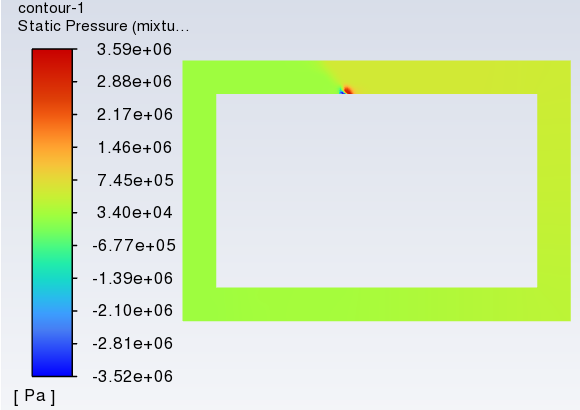
And I found large pressure in the domain. Can it can demonstrate it to some extent?
-
-
July 22, 2024 at 9:19 am
Rob
Forum ModeratorYes. In CFD the maths will conserve mass. The domain size is fixed. If density is temperature dependent where is the volume going to go? In theory you can set temperature dependent liquid density & ideal gas but that'll still cause problems as you try and boil the liquid: Fluent doesn't allow temperature & pressure dependent density other than idea or real gas. Try patching a layer of vapour using ideal gas at the top of the domain & see how it behaves.
-
July 22, 2024 at 12:20 pm
Dato
SubscriberThank you Rob. You have imparted some unique knowledge about Multiphase and I have benefited from it a lot. Thanks.
-
- The topic ‘Strange Divergence in natural circulation simulation simulation using VOF’ is closed to new replies.



-
5649
-
1885
-
1404
-
1303
-
1021

© 2026 Copyright ANSYS, Inc. All rights reserved.