-
-
June 5, 2023 at 9:53 am
Iuliia Riabenko
SubscriberDear sir!
Please help me! I start to learn Zemax and Lumerica.
I sdtudy the article https://optics.ansys.com/hc/en-us/articles/360042097313-Metalens
And I have questions:
- Zemax allows me to create phase mask using Binary 1. Why Binary 1 does plase befor cylidrical lens
 . Then we optimaze to get focus point
. Then we optimaze to get focus point  . This give the phase distribution in binary 1.
. This give the phase distribution in binary 1.  And I can save this data in txt file.
And I can save this data in txt file.  But how can I use them in Lumerical?
But how can I use them in Lumerical? - How the phase_map_from_ZOS_R100um.mat has been create? And which comand sread data from it and compare it with data from metaatom phase data (EH_and_phase_vs_radius_interp_fdtd.mat)?
Best regards,
Iuliia
- Zemax allows me to create phase mask using Binary 1. Why Binary 1 does plase befor cylidrical lens
-
June 5, 2023 at 8:29 pm
Guilin Sun
Ansys EmployeeIt seems the main questions are for Zemax. Please submit your question here: https://community.zemax.com/
Interoperation of Zemax and Lumerical for metalens is: Lumerical FDTD simulates elements to design the metalens, and then simulate the metalens to get field result under given illumination (steps 1~3 in "overview"). Then the result is imported to Zemax for raytracing.
-
June 6, 2023 at 11:11 am
Iuliia Riabenko
SubscriberThank you for your answer. I clear undestand Zemax part. In which file need I enter phase data which I get from Zemax? How did you create the files: phase_map_from_ZOS_R100um.mat, EH_and_phase_vs_radius_interp_fdtd.mat and EH_and_phase_vs_radius_interp_rcwa.mat?
-
June 6, 2023 at 11:43 am
-
June 6, 2023 at 3:59 pm
Guilin Sun
Ansys EmployeeLumerical has script command "matlabsave" to save variables created from Lumerical products. Please refer to
https://optics.ansys.com/hc/en-us/articles/360034928113-matlabsave-Script-command
The simulation methodology for metalens is first to use FDTD/RCWA simulation to create the metlens and data, and then export. Zemax will import the created data. It is better to follow the steps described in the website example you referred. If you have questions at at step, please let me know.
-
June 6, 2023 at 6:24 pm
Iuliia Riabenko
SubscriberThank you.
How could I implement the next statment "complex systems, where analytical solutions don’t exist or would be hard to calculate, we can design the ideal phase mask in OpticStudio using the ray tracing and optimization capabilities."?How can I add this data to matlab file to use them it step 3? Where do you take the target phase profile for step3?
-
June 23, 2023 at 3:04 am
nauval.afif
SubscriberHi,
I understand how the files EH_and_phase_vs_radius_interp_fdtd.mat and EH_and_phase_vs_radius_interp_rcwa.mat were created (using Lumerical Scripting File), but I still don't understand how the file phase_map_from_ZOS_R100um.mat has been created. Based on the name I think the file should have been generated from OpticStudio but I don't know how to do it. Please give me more information.
Thank you.
-
June 23, 2023 at 8:46 pm
Guilin Sun
Ansys Employee"complex systems...." is for phase distribution is not spherical and no analytical expression then you will need Zemax for help. You only need to extract the wavefront infomation, the phase distribution from Zemax.
"phase_map_from_ZOS_R100um" is the target phase_map. You can use whatever software to create it and save it in .mat:

-
July 3, 2023 at 2:27 am
nauval.afif
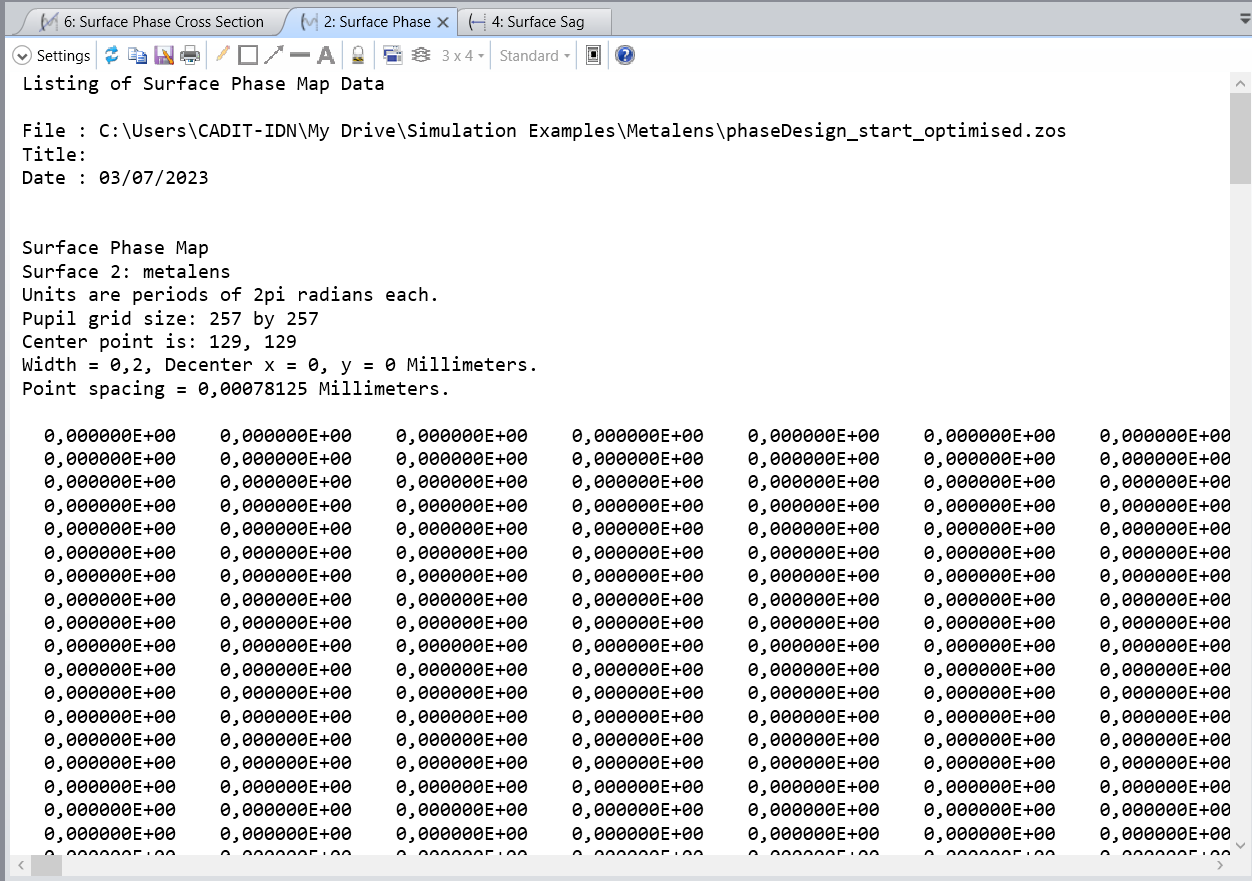
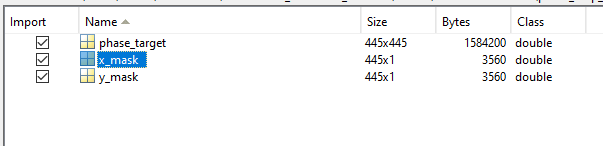
SubscriberI am still confused, the size of phase_target in "phase_map_from_ZOS_R100um.mat" is 445 x 445. But the surface phase map from the optimized "phaseDesign_start.zar" is only 257 x 257. At first glance also, the numbers look very different. Could Ansys please give more detailed information about this? The information in the metalens application gallery is too concise and not that detailed. Thank you,
-
July 4, 2023 at 2:20 pm
Guilin Sun
Ansys EmployeeThey are different and not necessarily the same dimension. "phase_map_from_ZOS_R100um.mat" is for FDTD use.
-
July 14, 2023 at 1:34 pm
-
July 14, 2023 at 2:07 pm
Iuliia Riabenko
SubscriberOk. I undestand. This is coordinate where phases were menshed. It's come from Zemax semi-diameter.
-
-
July 14, 2023 at 2:33 pm
Iuliia Riabenko
SubscriberPlease exmlaine me these structures:
If I clear undestand these data come from FDTD(or RCWA calculation) which has been done for the Pillars with different radius. That why numbers of E(or H)
 is equal 361. Then we have the 9 points with coordinate
is equal 361. Then we have the 9 points with coordinate  in X and Y direction. Each point corresponding to the Electrical Filed and Magnetical Field in the First Frenel Zone
in X and Y direction. Each point corresponding to the Electrical Filed and Magnetical Field in the First Frenel Zone  . The number 1,2,3..., 361 is indexs which link the radius data of Pilars and the Electromagnetic Field in near region
. The number 1,2,3..., 361 is indexs which link the radius data of Pilars and the Electromagnetic Field in near region  .
. How can I calculate phase which describe by one number from -pi to pi using the 18 values of Fields?
-
July 14, 2023 at 9:55 pm
Guilin Sun
Ansys EmployeeI would strongly suggest that you read the script file that creates the data. For example, in this file:
fdtd_unit_cell_export_phase_field.lsf
the data file is:
EH_and_phase_vs_radius_interp_fdtd.mat
use the following script:
matlabload("EH_and_phase_vs_radius_interp_fdtd");
EE=E.E;
?size(EE);
result:
3 3 1 1 361 3they represent x,y,z,f/lambda,phase and Ex/Ey/Ez.
Please check the data and see it is from which script file created and you will know the meaning of the dimensions.
-
July 19, 2023 at 1:44 pm
Muhammad Usman Afzal
SubscriberIn the first picture of zeemax by Iuliia Riabenko, “Why the radius is 1.578 and thickness is of 0.1 in biconic surface?
Is there any procedure to calculate?
Furthermore as per the article link shared by Muhammad Afif, “The obtained surface phase cross section response is different then shown in the shared metalens resource why is so much difference?”
-
July 19, 2023 at 7:48 pm
Guilin Sun
Ansys EmployeeFor Zemax questions please post in zemax forum https://community.zemax.com/
It seems both questions are for Zemax.
-
May 13, 2024 at 11:51 pm
Guilin Sun
Ansys EmployeeToday I get sometime to review this post again, and have the following comments:
Since most often the metalens simulation involves Lumerical FDTD/RCWA and Zemax OpticStudio, some people may get confused when reading the articles from both websites. The basic work flow is from Lumerical article: https://optics.ansys.com/hc/en-us/articles/360042097313-Small-Scale-Metalens-Field-Propagation
The first step is to get the theoretical, ideal phase distribution (space) desired for the metalens with given focal length. We call this as "target phase profile". If it is ideally spherical, cylinderical, or any other phase distribution that can be analytically obtained, or from a table, it is easy to directly get the phase distribution, with any number of sampling you want. If one cannot directly get the phase, you will need Zemax to create the desired phase. The phase data in OpticStudio is in the Surface Phase tool.
Please note that in this step, the sole goal is to get the target phase distribution. Therefore you can use whatever the tools you have at hand. If you use Zemax, OpticStudio has fixed sampling points, seemly 2^n+1 where n=4,5,6,.... the integer number. Here the OpticStudio is not used to simulate the metalens, again it is to get the desired target phase!
The rest is the same as the examples. When the design of the metalens is for normal incidence, in Zemax it has to be illuminated with collimate light, and in FDTD it has to use plane wave with incident angle zero for simulation.
-
- The topic ‘Metalens’ is closed to new replies.



-
5139
-
1831
-
1387
-
1248
-
1021

© 2026 Copyright ANSYS, Inc. All rights reserved.