-
-
March 1, 2022 at 1:22 am
wlane
SubscriberI was getting some odd results trying to run a basic structural simulation and while I've been able to sort it out, I can't figure out why it's an issue. Any insight would be very appreciated!
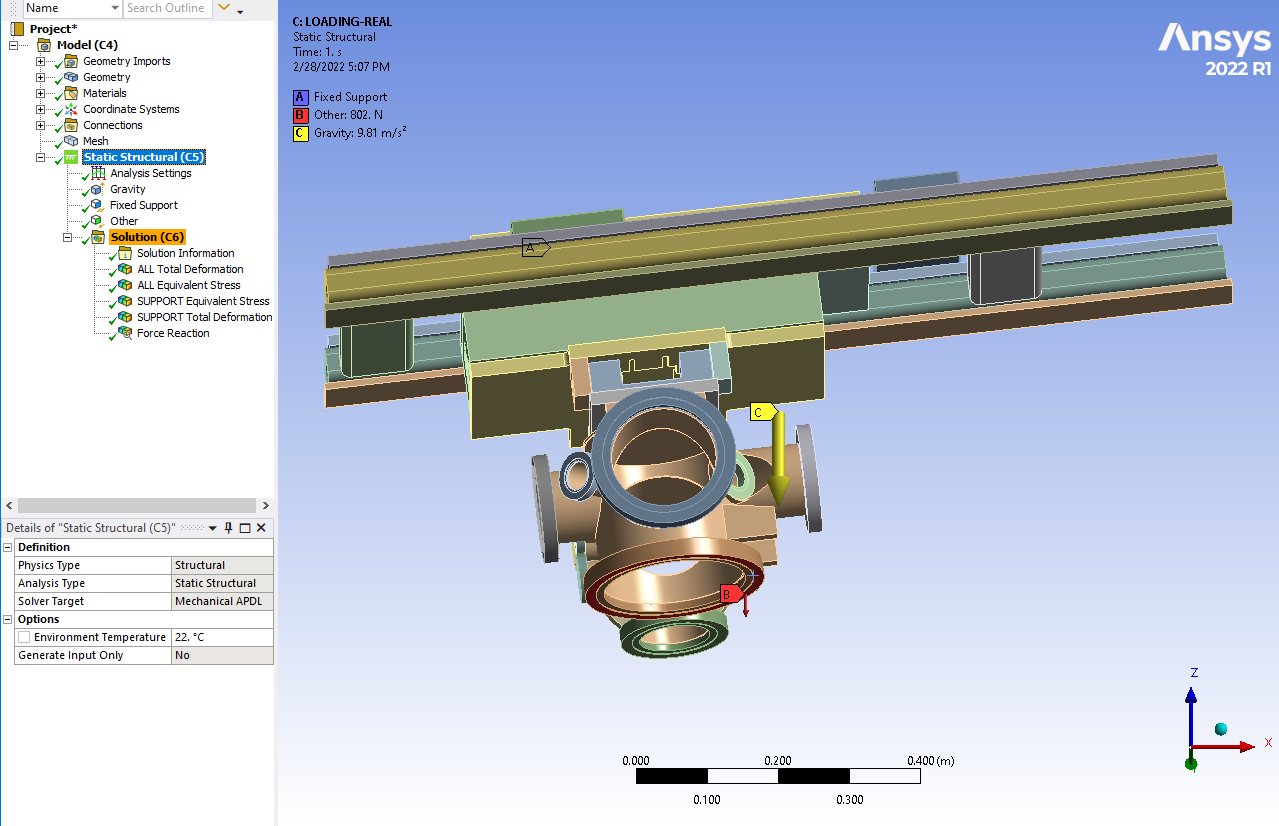
The only boundary conditions applied to the system are gravity [0,0,-9.81] m/s^2 and fixed supports at the top. I added a force to the bottom face [0,0,-802] N. I ran the simulation and checked the reaction forces of the fixed supports and to my surprise, the reaction force is less than the combination of the gravity/mass and the added force. Turns out, it's exactly double the force. I flipped the force direction [0,0,+802] N (but kept gravity the same) and re-ran the simulation. With the reversed loading, the reaction forces balanced as expected. But the force vector that ANSYS displays literally shows it opposing the gravity vector, so I'm very confused about what's going on. I've attached some pictures to show the loading conditions and results.
Loading [0,0,-802] N
March 1, 2022 at 11:36 amMarch 1, 2022 at 5:18 pmwlane
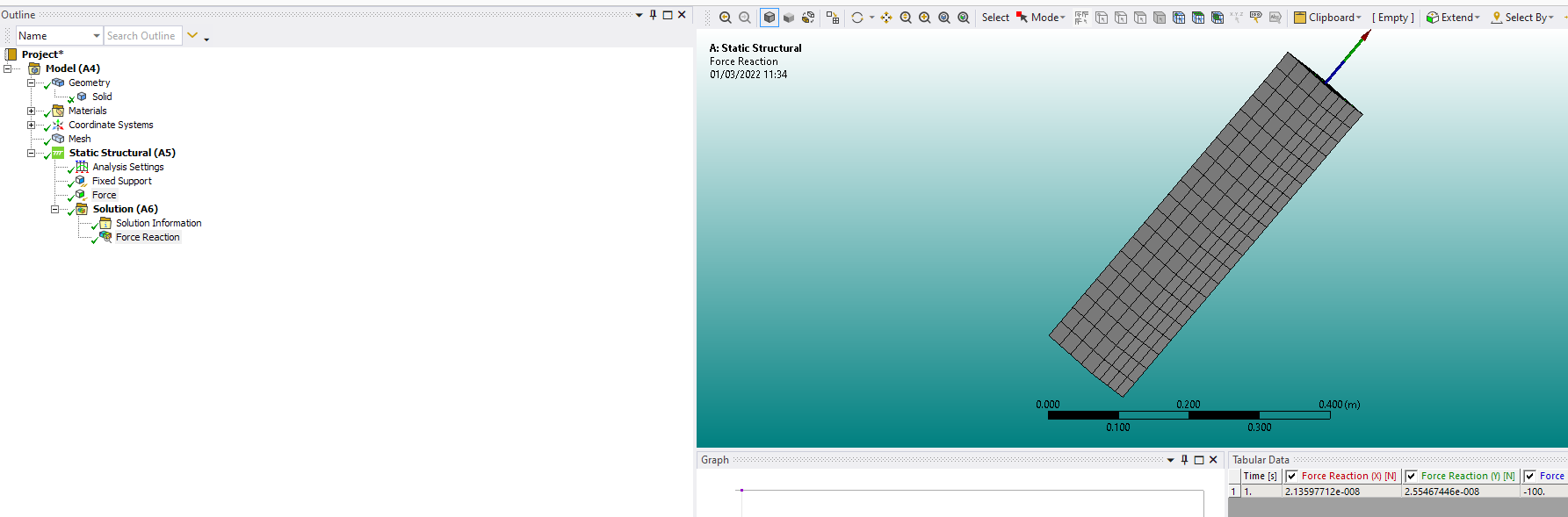
SubscriberErik Thanks for the response! That was actually the first thing I did when I couldn't find any other errors. With a simple beam the displacement, stress, reaction forces, etc. were all consistent with Euler-Bernoulli theory. Setup: 0.1m x 0.1m x 1m, Fixed @ 0m, F=[0,0,-1]kN @ 1m, E=200GPa yields a reaction force of [0,0,1] kN and max displacement of 0.2 mm.
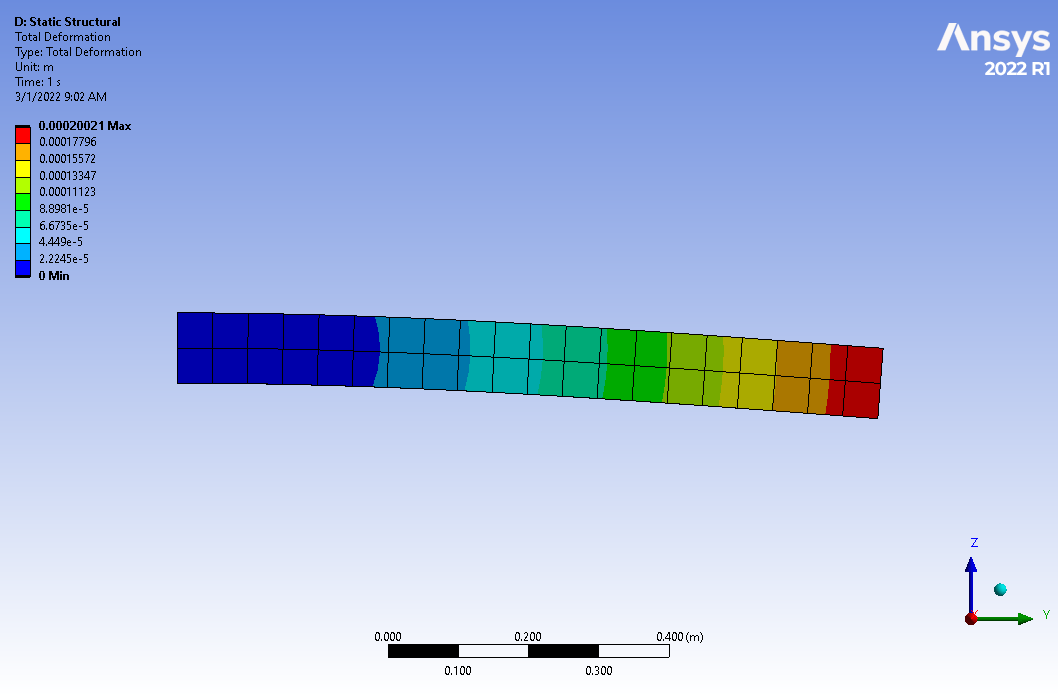
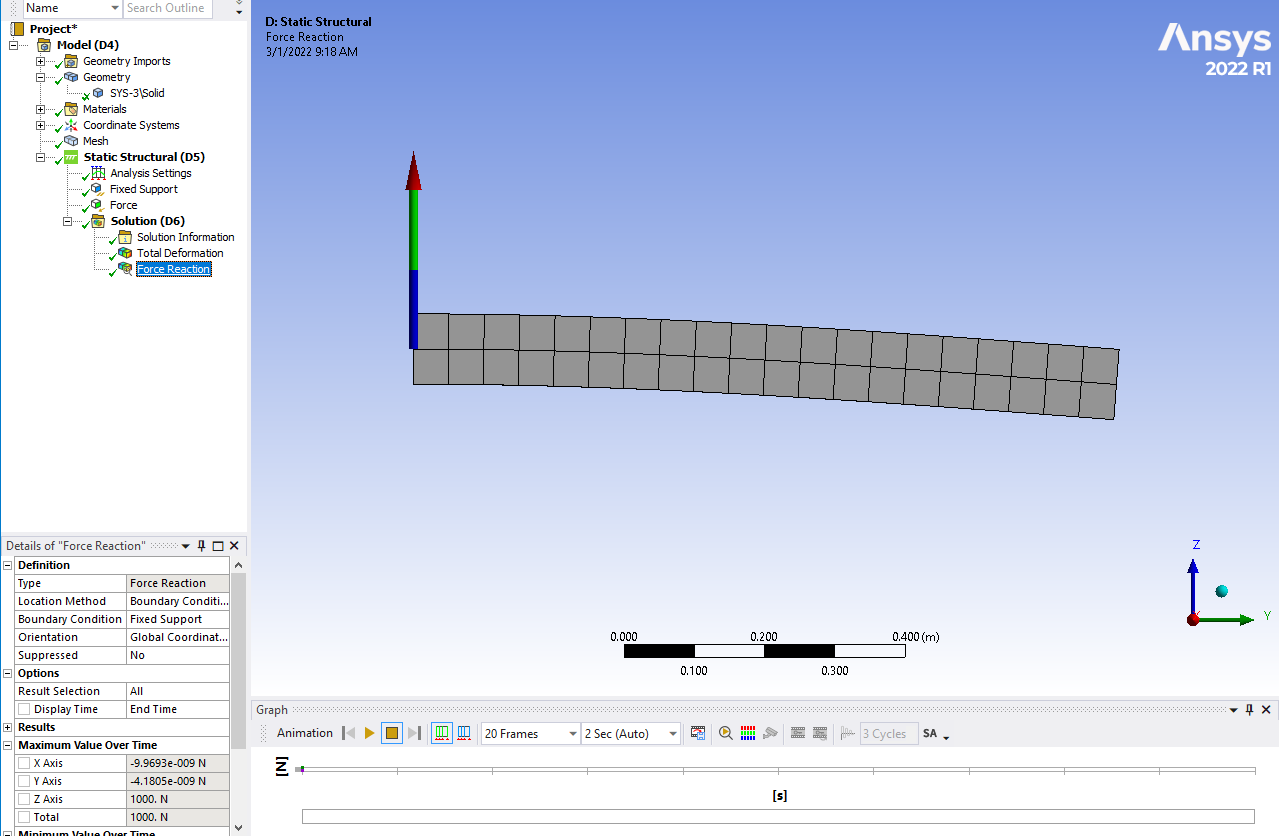
March 2, 2022 at 7:55 amErik Kostson
Ansys Employee
That is good.
Can we now take away all the loads, gravity and supports. Then add a fixed support (please show where it is scoped), and then just add a force of 100 N (show the details of the load please).
So we should only have a fixed support and a force (do not call it Other please).
Run that and see that we get equal and opposite reaction in the fixed support.
All the best
Erik
March 2, 2022 at 8:18 pmwlane
SubscriberErik Thanks again for the support! After simplifying down to only the supports and running a combination of different loading conditions I have finally identified the issue. Instead of using the built-in Standard Earth Gravity conditions, I used the generic Acceleration condition with components [0,0,-9.81] m/s^2, thinking this would be equivalent, but that's not the case. You need to accelerate the bodies upward to feel the opposing downward force. Once I figured this out I searched and found the following answer: /forum/discussion/11409/difference-between-standard-earth-gravity-and-acceleration
March 3, 2022 at 8:27 amErik Kostson
Ansys EmployeeHi
That is good - was thinking of that - all the best
Erik
Viewing 5 reply threads- The topic ‘Force seems to be applied in opposite direction’ is closed to new replies.
Ansys Innovation SpaceTrending discussions- The legend values are not changing.
- LPBF Simulation of dissimilar materials in ANSYS mechanical (Thermal Transient)
- Convergence error in modal analysis
- How to model a bimodular material in Mechanical
- APDL, memory, solid
- Meaning of the error
- Simulate a fan on the end of shaft
- Nonlinear load cases combinations
- Real Life Example of a non-symmetric eigenvalue problem
- How can the results of Pressures and Motions for all elements be obtained?
Top Contributors-
3912
-
1414
-
1256
-
1118
-
1015
Top Rated Tags© 2025 Copyright ANSYS, Inc. All rights reserved.
Ansys does not support the usage of unauthorized Ansys software. Please visit www.ansys.com to obtain an official distribution.
-


Ansys Assistant

Welcome to Ansys Assistant!
An AI-based virtual assistant for active Ansys Academic Customers. Please login using your university issued email address.
Hey there, you are quite inquisitive! You have hit your hourly question limit. Please retry after '10' minutes. For questions, please reach out to ansyslearn@ansys.com.
RETRY