TAGGED: ansys-explicit
-
-
July 22, 2021 at 9:18 am
mhfitri
SubscriberHi guys.
I would like to ask regarding how do we interpret reaction force to gain action force for some rear structure. Please kindly correct me if i am wrong.
July 24, 2021 at 2:24 pmmhfitri
SubscriberIs there anyone can help me clarify, please?
July 24, 2021 at 7:02 pmpeteroznewman
SubscriberWhen designing an energy absorbing system, start by defining the kinetic energy (KE) before impact.
KE = 1/2*mass*(impact_velocity)^2
What is the mass of the moving object? What is the impact velocity?
At the end of the event, do you want the moving object to elastically rebound off the structure with the same velocity it came in with, or do you want the structure to crumple/crush to absorb all the KE so that the moving mass comes to rest? Or you can have some rebound and some crumpling/crushing.
Depending on your answer to that question, there are different designs of energy absorbing systems.
Also, you should reply to the email sent to confirm your email address so that you have the full functionality of the site.
July 25, 2021 at 5:26 ammhfitri
SubscriberHi peteroznewman Thank you for your reply.
Regarding the confirmation, yes i did not notice on that email, already done it, thank you for reminding.
For the kinetic energy, yes i did. Just for observing the effect of the rubber, i was testing the mass of 10kg moving with a speed of 14m/s to gain about 1000 J of energy for the impactor. Even though i was looking at how the certain mass change moving at the same speed affect the rebound ability, i also wish to note how much the force transferred to the hollow behind during maximum compression of the rubber.
For now the goal if the amount of the reaction for at the probe-fixed support is the correct amount of force transferred to the rear hollow. Example if the amount of reaction force is 2000 N, can i just use the same force and apply it for the hollow at Static Structural?
July 25, 2021 at 10:38 ampeteroznewman
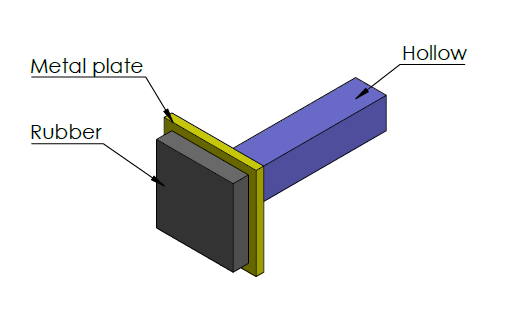
SubscriberIf you have a model of the system and solve it in Explicit Dynamics, you will be able to measure the reaction force at the fixed end of the hollow tube. Do not leave the hollow tube out and apply the fixed support on the back of the plate, that will not be the same reaction force at all.
For an elastic hollow tube structure behind the elastic rubber/metal plate, you can't remove the hollow tube from the system and just impact the rubber/plate and get the same reaction force. Below I explain why.
The way to think about this is springs in series. There is the spring rate of the rubber Kr, the spring rate of the plate Kp, and the spring rate of the hollow tube Kt.
The equivalent spring rate Keq is computed from the springs in series equation:
1/Keq = 1/Kr + 1/Kp + 1/Kt
The peak force on the hollow tube occurs when all the KE is converted to Potential Energy PE stored in those springs.
PE= 1/2*Keq*Xmax
where Xmax is the distance the moving mass travels after impact before its velocity becomes zero.
You can solve for Xmax by setting PE = KE.
But first you need to know Keq. Use a Static Structural analysis, apply a small displacement Xu to the face of the rubber and output the reaction force Fu. Now you can calculate Keq = Fu/Xu.
A good estimate of the maximum force Fmax = Keq*Xmax.
You can see that if you leave Kt out of the calculation of Keq, the estimated force will be much larger.
Viewing 4 reply threads- The topic ‘Action – Reaction Force’ is closed to new replies.
Innovation SpaceTrending discussionsTop Contributors-
4959
-
1639
-
1386
-
1242
-
1021
Top Rated Tags© 2026 Copyright ANSYS, Inc. All rights reserved.
Ansys does not support the usage of unauthorized Ansys software. Please visit www.ansys.com to obtain an official distribution.
-
The Ansys Learning Forum is a public forum. You are prohibited from providing (i) information that is confidential to You, your employer, or any third party, (ii) Personal Data or individually identifiable health information, (iii) any information that is U.S. Government Classified, Controlled Unclassified Information, International Traffic in Arms Regulators (ITAR) or Export Administration Regulators (EAR) controlled or otherwise have been determined by the United States Government or by a foreign government to require protection against unauthorized disclosure for reasons of national security, or (iv) topics or information restricted by the People's Republic of China data protection and privacy laws.