-
-
October 10, 2020 at 11:44 am
Rameez_ul_Haq
SubscriberOctober 10, 2020 at 1:28 pmpeteroznewman
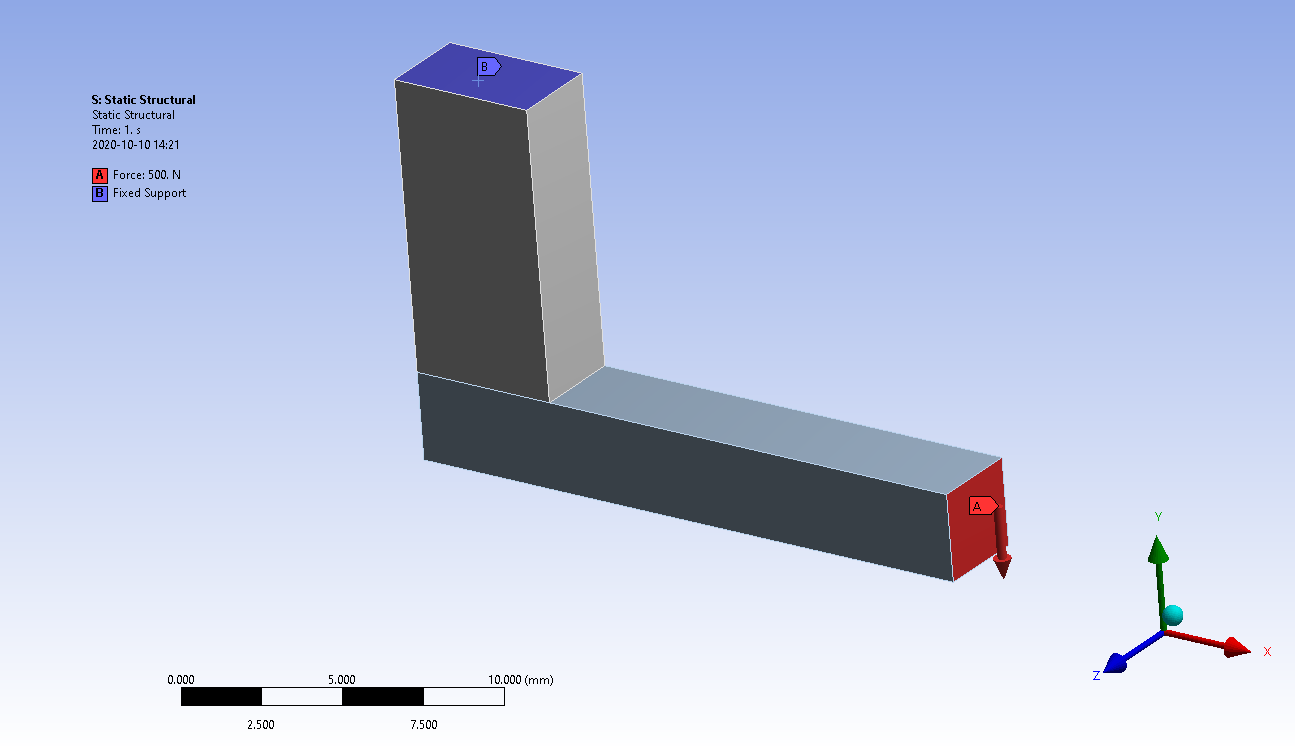
SubscriberArraynThe green face is going to move in Y, but it is also going to move in X and rotate about Z. That means the nodes along the right edge of the green surface will reach 2 mm of Directional Deformation along Y before the nodes along the left edge.nWhen you say stop the motion of each and every node on that surface, it seems you want the solution to continue to apply load, but those nodes stop. The way to do that is to use a Frictional (or Frictionless) Contact with an object you would add to the model.nI recommend you create a Multibody part and use Shared Topology to connect the two blocks. Don't use Bonded Contact. That will leave the green surface free to be used in a Frictional Contact with an added part. That added part can be a surface 2 mm away from the green surface. It can be a Rigid surface. Use a Fixed Joint to hold that surface fixed.nYou can do the same with the X and Z direction. It sounds like the rigid surfaces will create a pocket.nOctober 12, 2020 at 6:59 amRameez_ul_Haq
SubscriberIsn't it a clever idea to give multiple contacts to the green surface? I mean bonded with the other solid and frictionless contact with the additional surface?October 12, 2020 at 8:14 ampeteroznewman
SubscriberIt's more clever the way I described because adding contacts increases the number equations that have to be solved, while Shared Topology reduces the number of equations that have to be solved.nIt will probably work if you try to use two contacts.nViewing 3 reply threads- The topic ‘Stopping a deforming geometry after a specific displacement.’ is closed to new replies.
Ansys Innovation SpaceTrending discussionsTop Contributors-
3712
-
1313
-
1163
-
1090
-
1014
Top Rated Tags© 2025 Copyright ANSYS, Inc. All rights reserved.
Ansys does not support the usage of unauthorized Ansys software. Please visit www.ansys.com to obtain an official distribution.
-
The Ansys Learning Forum is a public forum. You are prohibited from providing (i) information that is confidential to You, your employer, or any third party, (ii) Personal Data or individually identifiable health information, (iii) any information that is U.S. Government Classified, Controlled Unclassified Information, International Traffic in Arms Regulators (ITAR) or Export Administration Regulators (EAR) controlled or otherwise have been determined by the United States Government or by a foreign government to require protection against unauthorized disclosure for reasons of national security, or (iv) topics or information restricted by the People's Republic of China data protection and privacy laws.