Material Database — Lesson 2
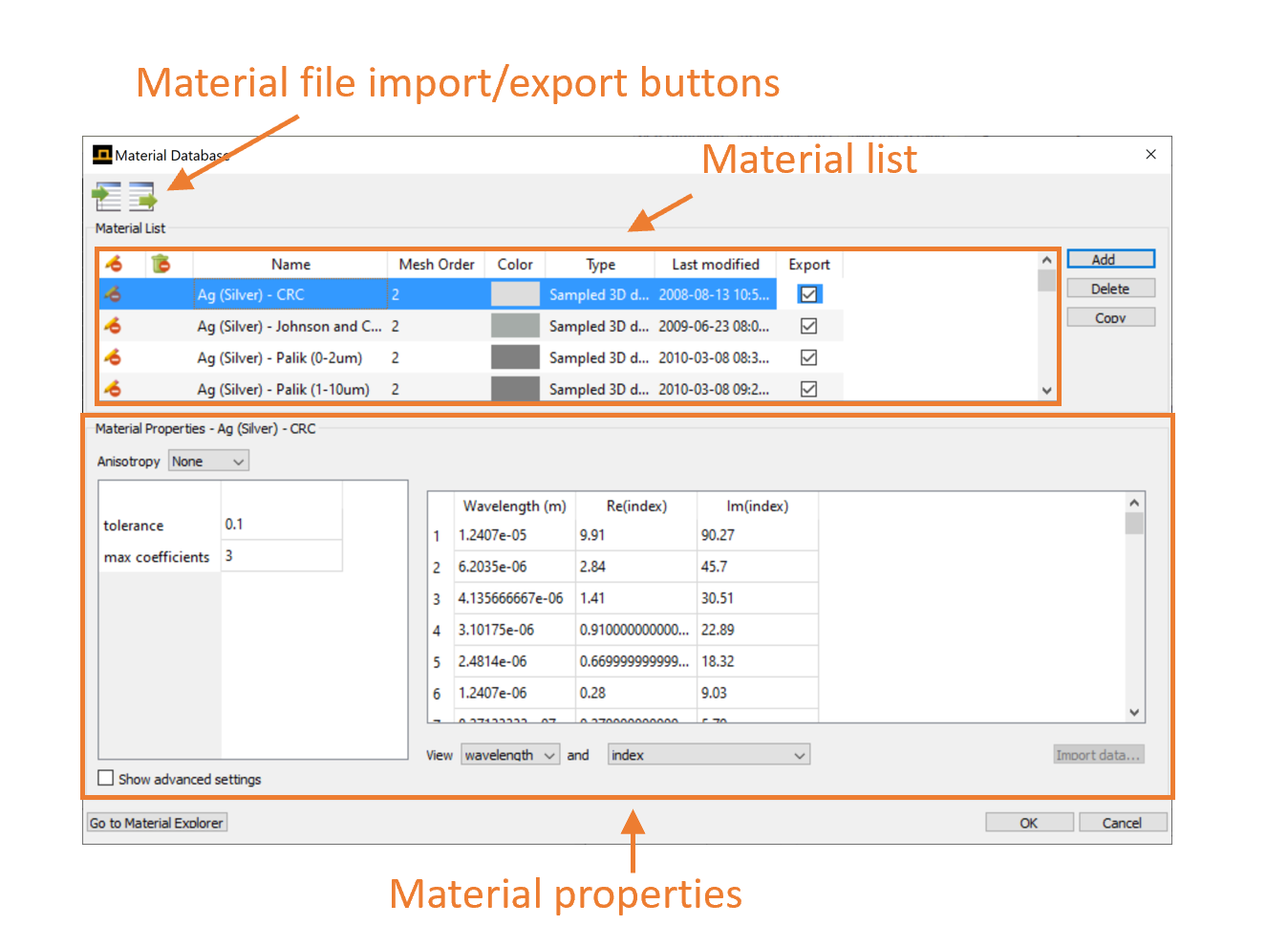
Material file import/export buttons: Import or export materials in the form of .mdf files
Material List:
- Write protect: Determines whether the material can be modified. To modify a write-protected material, first make a copy of that material.
- Referenced material: Tells you whether the material is currently being used by an object in the simulation
- Name: Material name
- Mesh order: The meshing priority
- Color: Color that the material will be rendered in the CAD viewports
- Type: Material model used to define the material
- Last modified: Time when the material was last edited
- Add/Delete/Copy buttons: add, delete, or create a copy of the selected material
Material properties:
- Lists the material parameters. The available parameters depend on the type of material model. The screenshot shows the parameters for a sampled data material, which includes a table of refractive index vs. frequency.
New materials can be defined from material models or from sampled data
Available material models
- Permittivity models
- Conductivity models
Any sampled material can also be added to the simulation. The following video which is also available in the link below from the Knowledge Base, describes how to import experimental material data into the Material database, and how to check the material fit with the Material Explorer. The Sampled 2D Data or Sampled 3D Data material type should be used when creating materials from measured data.
A wide variety of optical materials used in the Lumerical FDE come in the form of a wavelength-dependent (dispersive) complex refractive indices. In this video lesson, we will demonstrate how to import dispersive refractive index data from a text file into the Sampled Data material model.

