Quiz – Understanding Optical Specifications
Before beginning the quiz, please note that this course provides you with the opportunity to download a summary sheet from the corresponding summary lesson. You may use the summary sheet to assist you in answering quiz questions.
Please note that you only have 5 attempts to pass this Quiz.
Quiz Summary
0 of 7 Questions completed
Questions:
Information
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading...
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You must first complete the following:
Results
Results
0 of 7 Questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 point(s), (0)
Earned Point(s): 0 of 0, (0)
0 Essay(s) Pending (Possible Point(s): 0)
Categories
- Not categorized 0%
-
Unfortunately, you did not pass the quiz.
Don't be discouraged - Go through the course material including the lecture videos, handout slides, and simulation examples to prepare and try again.
-
Congratulations, you have passed the quiz!
You still have room for improvement - Review the slides and simulation examples again to identify the concepts that you may have missed.
-
Congratulations, you have passed the quiz!
You scored better than average, but if you are still unsure about a particular topic, try starting a discussion on the Ansys Learning Forum to discuss your questions with peers around the world.
-
Congratulations, you have passed the quiz!
You did great - Check out other courses to further your knowledge. Also, visit the Ansys Learning Forum and participate in discussions on this subject to help your peers and deepen your own knowledge.
-
Congratulations you have passed the quiz!
You have excelled on this topic - Check out other courses and see if you can ace them too. Also, visit the Ansys Learning Forum to help your peers on this topic. With your knowledge, you can make a real difference.
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- Current
- Review
- Answered
- Correct
- Incorrect
-
Question 1 of 7
1. Question
You are considering buying a lens. You have shortlisted three lenses with the same effective focal length
and f/#s of 1.4, 5, and 10. The goal of your project is to produce highest possible resolution. Which lens
should you choose?
All three lenses are magical and do not experience any aberrations.CorrectIncorrect -
Question 2 of 7
2. Question
Two small circular objects are imaged through a lens. The image appears blurry at the edges. Which physical phenomenon is responsible for this blur?
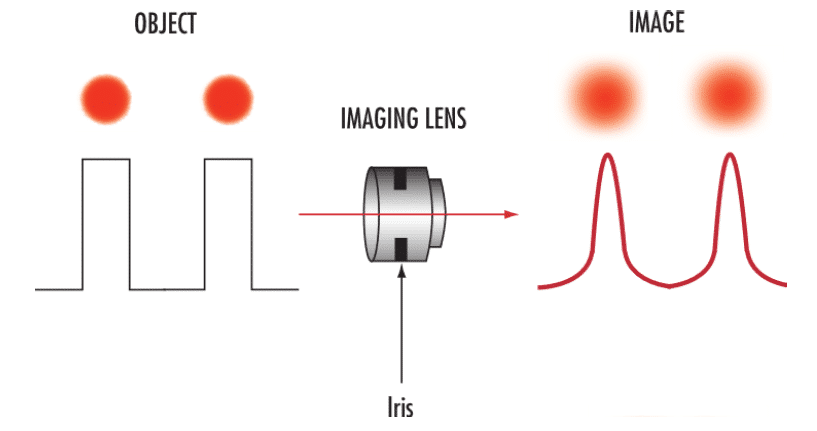 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 3 of 7
3. Question
You have just purchased a brand-new diode laser that generates radiation at 520 nm. You want to focus
the light to the tightest possible spot with a lens (f/4) that you already own. What will the Airy disk
diameter of this spot be?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 4 of 7
4. Question
Which of the following factors does not play any role in determining the diffraction-limited resolution of an
imaging system?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 5 of 7
5. Question
What working f/# was used to generate the following Airy disk? Assume there are no aberrations.
Hint: the wavelength is listed in the image below as 0.55 μm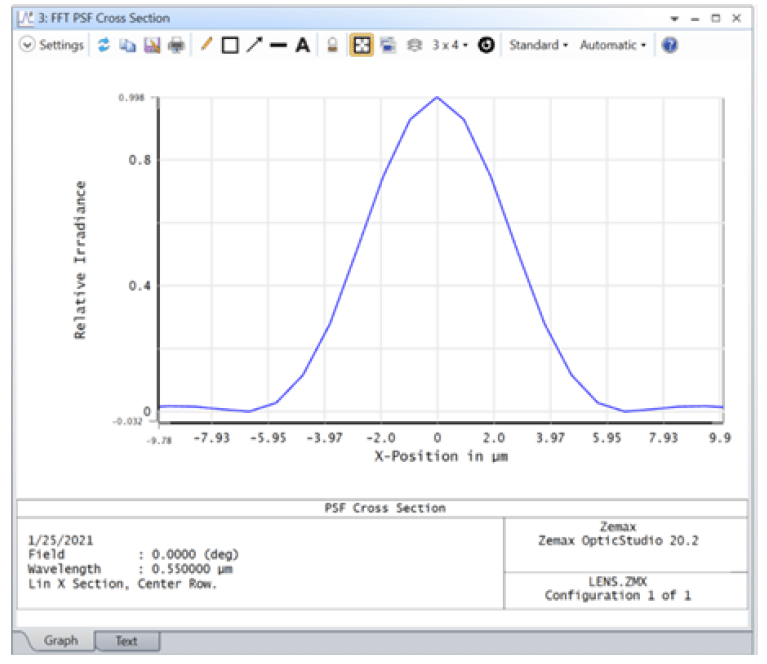 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 6 of 7
6. Question
You have purchased an oil immersion (n=1.51) microscope objective with a numerical aperture of 1.40.
What is the angular extent of the light cone that can be captured by this objective?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 7 of 7
7. Question
The Sony ICS 625 sensor consists of an array of 2448 × 2050 pixels where each individual pixel has a
size of 3.45 μm. What is the image space resolution of this sensor in lp/mm?CorrectIncorrect
